PAKISTANI student Aqsa Shabbir is hot, tired and frustrated. A keen field hockey player, she can no longer train during the day because of a brutal heatwave, she can’t sleep at night and she fears that she will not play well in a tournament at the end of the month.
The 17-year-old, who lives in Jacobabad in the southern Sindh province, already had to overcome obstacles – like many girls who live in Pakistan’s smaller cities where exercising in public is frowned upon – and the heatwave is making things harder.
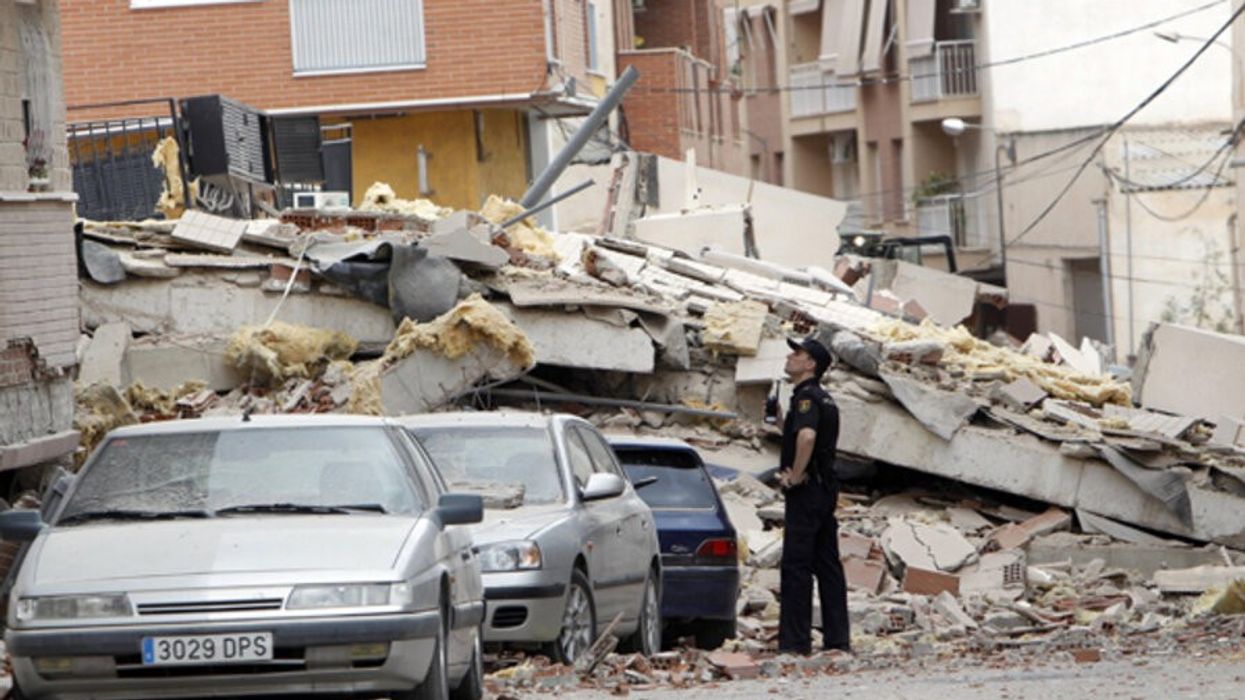
Two years ago, Jacobabad was named the hottest city on earth after temperatures there reached 51ºC (124ºF). This year, as a heatwave seared southeast Asia, temperatures shot up to 52ºC (126ºF) in May. “We cannot keep waiting for the weather to get better – it won’t,” Shabbir told the Thomson Reuters Foundation from Jacobabad.
Rising temperatures are one more barrier for women and girls who want to stay active in a country where there are few training spaces available to them, apart from private sports clubs reserved for the wealthy.
A 2022 study found that the main obstacles to participating in sport in the Muslim-majority country are “religious and cultural limitations, a lack of permission from parents, and a lack of sports facilities and equipment”.
Now add extreme heat, linked to climate change, to the list.
Shabbir is a member of the Star Women's Sports Academy in Jacobabad, the only women’s sports club in the city of nearly 300,000 people. The girls have started to train later in the day in a bid to beat the searing heat, but parents are unhappy with their daughters returning home late on their own.
And there is little rest at night either. Shabbir says the one air-conditioner her family has invested in provides “little comfort” because of frequent power cuts. The long days and nights are affecting her performance. “I am not playing my best,” she said. Haseena Soomro, who plays hockey at the same club, is equally frustrated.
“Of course the heat impacts our game,” the 19-year-old said. “The heat makes you sluggish, and this game is defined by speed.”
Sport has long been an often unaffordable luxury for girls from low-income households in Pakistan. It costs money to get to the few sports clubs available and even eating well is costly.
Some sports clubs try to help out with expenses but Erum Baloch, who founded the club in Jacobabad where Shabbir and Soomro play, says that can also be difficult.
And now she is also grappling with the challenge of training her team on outdoor pitches during what she calls the “long and unbearable” summers.
The situation is complicated by the fact that the women wear long clothing when training. Even though Baloch’s club is in a women’s government college, the girls she coaches are uncomfortable swapping their shalwar kameez [traditional outfits of long tunics paired with baggy trousers] for jogging pants, never mind cooler shorts.
“Families don’t like them wearing pants … shorts is too far-fetched a concept,” said Baloch. “Until society is ready, we need to concentrate on (making) sports for women acceptable instead of letting a dress come in our way.”
Farwa Batool, from Khairpur city in Sindh, wears long sleeves beneath her T-shirt to cover her arms. She also wears a hijab when she plays field hockey. “You cannot imagine the heat we bear,” she said, adding that she envies the men who can wear just shorts and T-shirts.
She gets up at 5.45am to train at the mixed gender club, hoping no men will be around. “If we could have women-only grounds, or women timings are introduced with men strictly not allowed, we too can be free of yards of cumbersome clothing.”
In Jacobabad, Baloch is hoping to get financing from the government or a sponsor to pay for an indoor facility with air conditioning.
Zamzam Allahbuksh said she pays out of pocket to top up water and ice supplies at the women’s sports club she runs in Mirpurkhas, 230 km (143 miles) east of Pakistan’s largest city Karachi. “I don’t want them suffering a heatstroke,” she said.
To manage costs, she has introduced games like football and volleyball because she does not have enough equipment for everyone to play cricket or field hockey.
“At least with one football or one volleyball, quite a few girls can play a sport,” she said.
Baloch, too, arranges for drinking water every day for her 43 field hockey players along with oral rehydration solutions but this is not sustainable.
“I don’t know how long I can carry on doing this,” she said. “We cannot train girls on an ad hoc basis – there needs to be a continuous and full government support for them, if they want to play their best.”
As heat threatens the viability of the few facilities that are available to women and girls, Baloch said she hopes they don’t lose out on the opportunities sports can provide.
Some of the athletes Baloch has coached went on to attend university on sports scholarships. Bushra Arif, a former field hockey player, is keenly aware of what sport offers girls in her country.
“Sports teach lifelong values like endurance, teamwork, confidence, overcoming challenges,” said Arif, now the director of physical education at Khursheed Begum Girls Degree College in Hyderabad in Sindh.
Despite all the challenges, Shabbir is trying to look on the bright side ahead of her important tournament in the neighbouring Sukkur district.
“Who knows, we may outdo teams from other cities with relatively lower temperatures, being more acclimatised to this extreme heat,” she said.