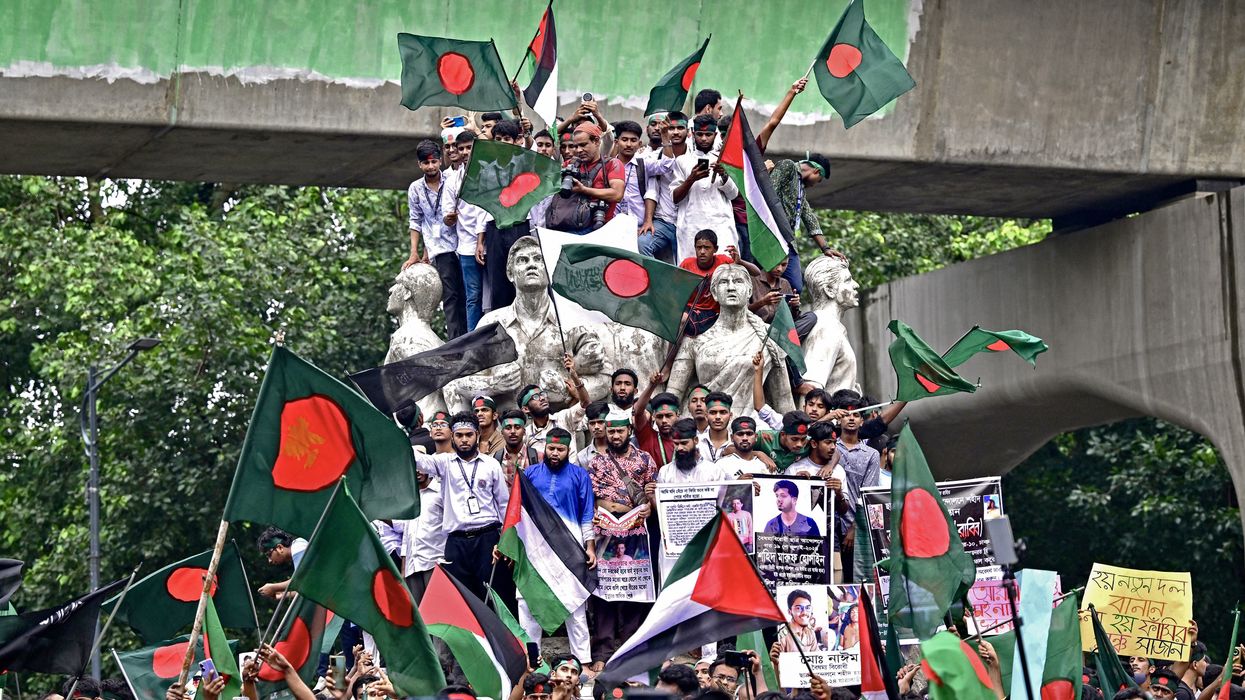
BANGLADESH’S interim government said it has no plans to ban the political party of ousted prime minister Sheikh Hasina, putting it at odds with the student revolutionaries who overthrew her in an uprising last year.
Hasina’s Awami League was accused of extensive human rights abuses during her 15-year tenure, including a violent crackdown on last year’s protest movement that killed more than 800 people.
Student leaders still grieving the deaths of their comrades have demanded the party, which played a pivotal role in Bangladesh’s bloody 1971 independence war under Hasina’s father, be outlawed.
But Nobel prize winner Muhammad Yunus, the de facto leader of the caretaker government that took office after her toppling, said it had no intention of doing so.
“Professor Yunus stated that the interim government has no plans to ban the party,” said a government statement issued late last Thursday (20). “However, individuals within its leadership who are accused of crimes, including murder and crimes against humanity, will be tried in Bangladesh’s courts.”
A tribunal in Dhaka has already issued arrest warrants for Hasina, who took refuge in India after her toppling, and her allies.
A fact-finding mission from the UN rights office said last month that her government was responsible for systematic attacks and killings of protesters in an attempt to hold onto power last year.
It found “reasonable grounds to believe that the crimes against humanity of murder, torture, imprisonment, and the infliction of other inhumane acts have taken place”.
Since she was toppled, students have consistently demanded the party be banned ahead of elections for a new government, expected by June next year.
The interim government did ban the Awami League’s student wing last October, citing its involvement in violent attacks on last year’s protests, while leaving open the fate of its parent organisation.
Hasnat Abdullah, one of the leading figures of a new studentbacked political party, planning to contest the next polls, slammed the government’s decision.
“The Awami League has to be banned,” he wrote on Facebook. Fellow student leader Nasir Uddin Patwary warned last month that failure to ban the party “will push Bangladesh toward civil war”, according to local newspaper Prothom Alo.
Shafiqul Rahman, the leader of Bangladesh’s main Islamist party Jamaat, likewise wrote on social media last Friday (21) that people would not accept the party’s “rehabilitation”.