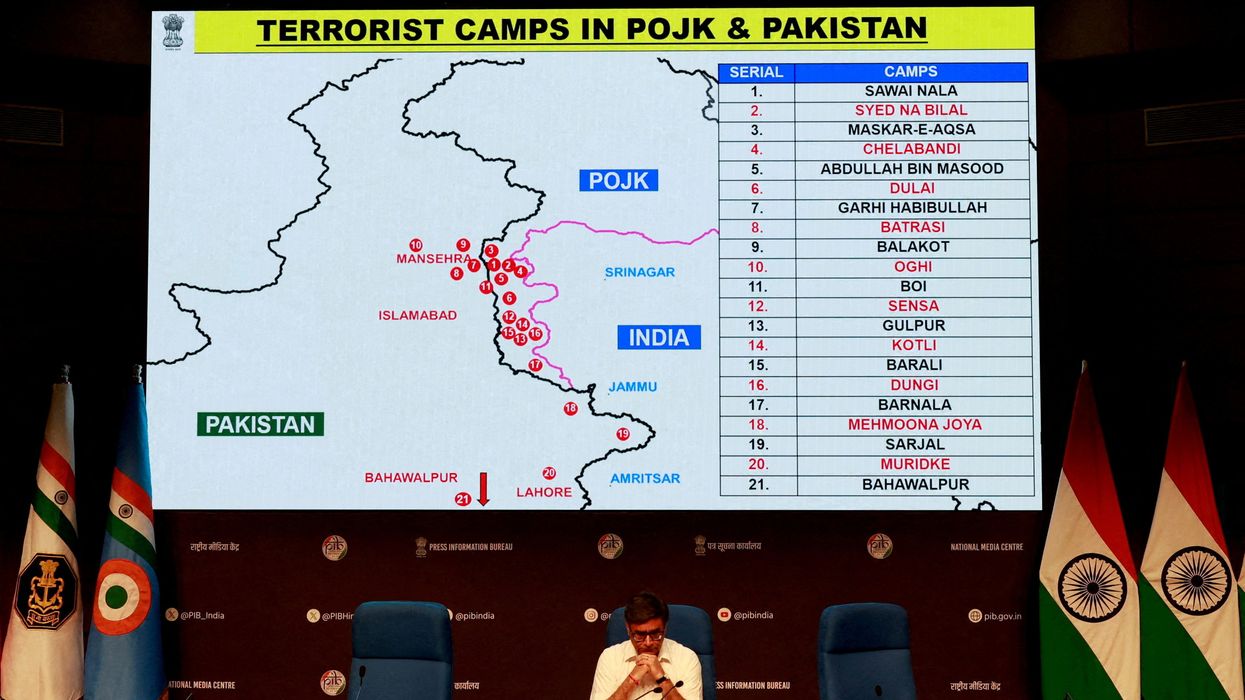
INDIA launched air and artillery strikes on Pakistani territory and Pakistan-administered Kashmir on Wednesday, in response to an attack on Indian tourists in Kashmir on April 22 that killed 26 people. Pakistan called the strikes a “blatant act of war” as tensions rose between the two nuclear-armed neighbours.
India said its military action, named Operation Sindoor, targeted nine sites used for what it described as “terrorist infrastructure” where attacks were planned.
What is Operation Sindoor?
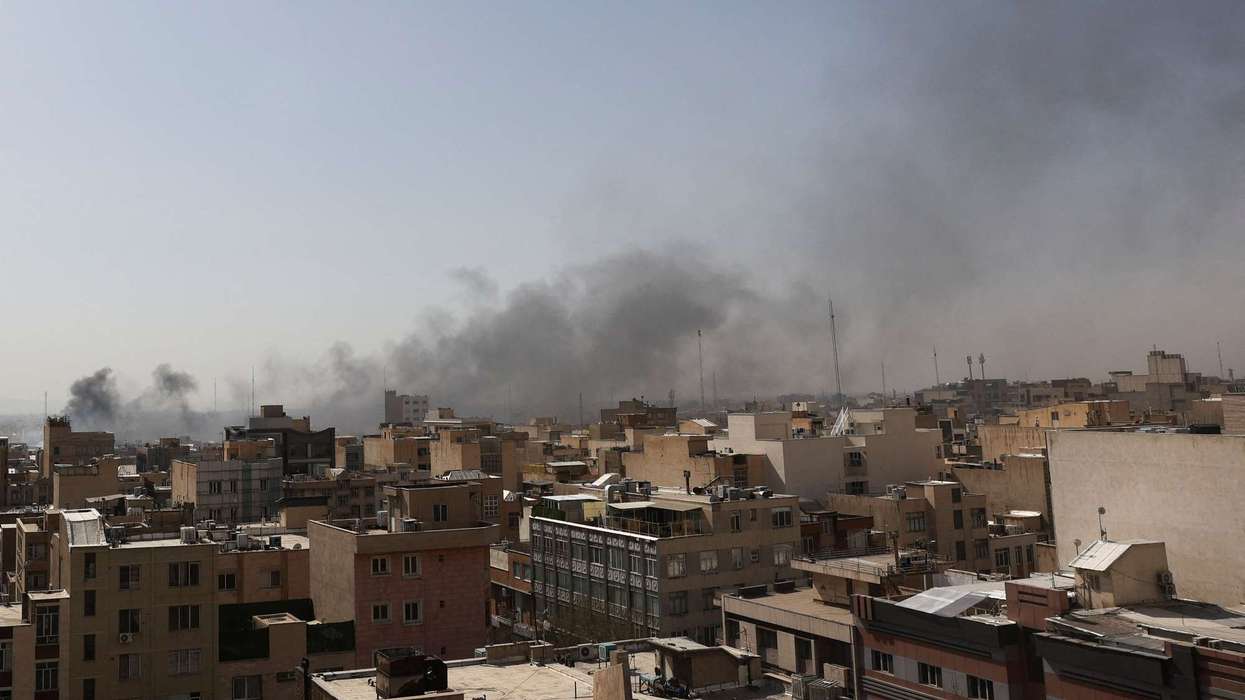
India launched Operation Sindoor on Wednesday, targeting what it described as “terrorist infrastructure” across nine locations in Pakistan and Pakistan-administered Kashmir. The action followed the April 22 attack on tourists in Indian-administered Kashmir that left 26 people dead.
India said the sites were used to organise attacks against it. The operation was named “Sindoor,” referring to the red vermilion worn by married Hindu women — a reference to the widows created by the April 22 killings, most of whom were Hindu men.
ALSO READ: India begins hydro work after suspending Indus Waters Treaty: Report
Islamabad said six locations were hit in Pakistan and a total of 24 impacts from different weapons were recorded. Pakistan called the strikes a “blatant act of war”.
Following the strikes, a Pakistan military spokesperson told Reuters that its forces shot down five Indian aircraft while they were still in Indian airspace. India has not confirmed this claim. Four local government sources in Indian-administered Kashmir told Reuters that three Indian fighter jets crashed in separate areas during the night. All three pilots were hospitalised, the sources said.
Both countries reported heavy exchanges of artillery fire along the Line of Control (LoC), the de facto border dividing Kashmir.
ALSO READ: India halts Pakistan imports as tensions rise over Kashmir killings
Casualties and local impact
Pakistan said eight people were killed, 35 injured and two missing as a result of India’s strike. India said seven civilians were killed and 35 injured in cross-border shelling by Pakistani troops.
Schools in parts of Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir were shut on Wednesday. In Pakistan’s Punjab province, authorities declared a state of emergency, placing hospitals and security agencies on high alert. Muzaffarabad, the capital of Pakistan-administered Kashmir, experienced power outages after the explosions.
ALSO READ: UN urges India-Pakistan restraint
Airspace and flight disruptions
India closed several airports and airlines including IndiGo and SpiceJet cancelled multiple flights. Air India diverted two international flights. Qatar Airways temporarily suspended flights to Pakistan. Pakistan International Airlines said flights in the air were rerouted to Karachi and those on the ground were held.
What triggered Operation Sindoor?
The operation followed a deadly attack on April 22 in Pahalgam, a tourist destination in Indian-administered Kashmir. The attack killed 26 civilians, most of them Hindu men. No group has claimed responsibility. India blamed the Pakistan-based group Lashkar-e-Taiba, a UN-designated terrorist organisation.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi accused Pakistan of supporting “cross-border terrorism” and gave the military “complete operational freedom” to respond. Pakistan rejected the accusation and said last week it had “credible intelligence” that India was preparing for a military operation.
Ongoing tensions and global reaction
India and Pakistan have fought multiple wars over Kashmir since 1947. Both countries claim the region in full but control parts of it. The last major escalation was in 2019 when 41 Indian paramilitary forces were killed in a suicide bombing blamed on a Pakistan-based group.
The United Nations called for “maximum restraint”. “The world cannot afford a military confrontation between India and Pakistan,” said UN spokesperson Stephane Dujarric. US Secretary of State Marco Rubio held discussions with both countries. China said it “regretted India’s military action” and expressed concern about current developments. Iran’s Foreign Minister Abbas Araghchi is expected in New Delhi after visiting Islamabad.
(With inputs from agencies)