by Amit Roy
EXHIBITION ABOUT JAMES COOK EXPLORES HIS LEGACY
WORD associations being what they are, when anyone mentions the surname “Cook” to me, I automatically think of former England cricket captain Alastair Cook, who has given India so much grief over the years.
But last week because of a new exhibition, The Voyages (until August 28) at the British Library, I was made aware of Capt James Cook, the explorer. Until recently he was what my more traditional colleagues at The Daily Telegraph would call “an all-round good egg”.
However, the exhibition suggests his three expeditions, which brought British colonisation in their wake, were not always an unqualified blessing to the remote islands that he visited.
If geography had been as fascinating as this when I was at school, I might well have eschewed the pleasures of physics later in life.
The exhibition marks 250 years since James Cook set sail from Plymouth in 1768 in the good ship Endeavour. The trip to the south Pacific lasted until 1771.
Charged by the Admiralty to undertake discoveries as close as possible to the South Pole, he undertook the second trip in HMS Resolution, from 1772-75.
The third, again in HMS Resolution, came as Cook was exploring the north Pacific from 1776-80.
The exhibition includes the original maps he drew, plus the evocative works of the artists who accompanied him. There is a painting depicting Cook’s ascent to paradise after he was killed in a fight with a group of Hawaiians at Kealakekua Bay on February 14, 1779.
In recent years, books on the pluses and minuses of the Raj by such authors as Kartar Lalvani and Shashi Tharoor have made us re-examine the chequered history of the British in India.
But most of us know very little of the impact of Cook’s three expeditions.
The Voyages pays tribute to Cook as the “greatest sea going explorer of all time”, but the British Library’s exhibition also – bravely, in my opinion – questions his status as a hero.
He did a lot of harm to the distant islands he “discovered” but which, in reality, had established civilisations long before Cook arrived.




 Nigel Farage
Nigel Farage Rupert LoweGetty Images
Rupert LoweGetty Images
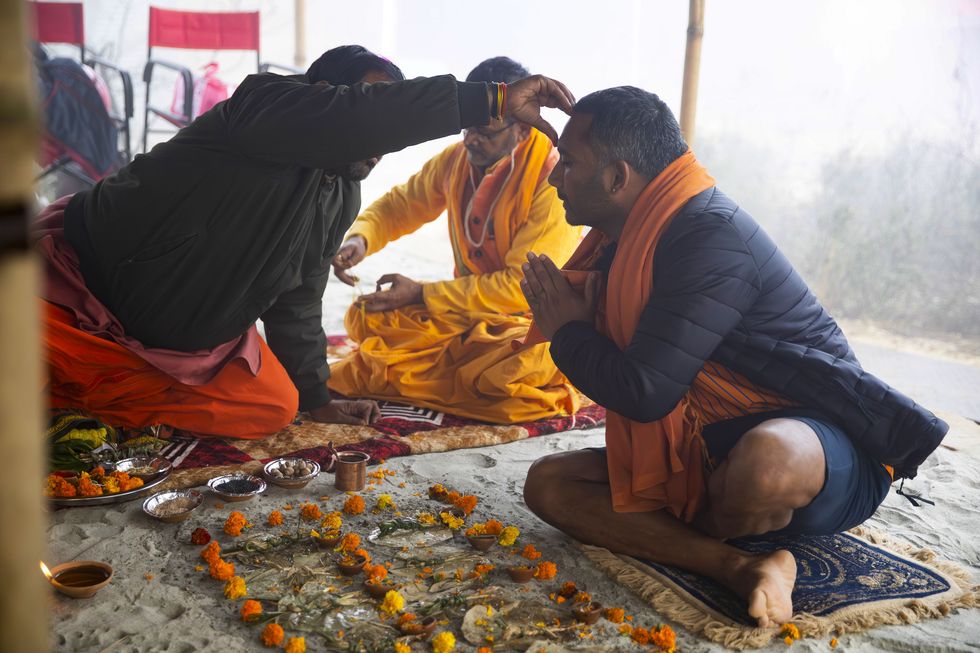








 Rajan offers the pind daan in honour of his father and ancestors
Rajan offers the pind daan in honour of his father and ancestors 


 LONDON, ENGLAND - JUNE 22: Baroness Floella Benjamin speaks during the unveiling of the National Windrush Monument at Waterloo Station on June 22, 2022 in London, England. The photograph in the background is by Howard Grey. (Photo by John Sibley - WPA Pool/Getty Images)
LONDON, ENGLAND - JUNE 22: Baroness Floella Benjamin speaks during the unveiling of the National Windrush Monument at Waterloo Station on June 22, 2022 in London, England. The photograph in the background is by Howard Grey. (Photo by John Sibley - WPA Pool/Getty Images)
 Ed Sheeran and Arijit Singh
Ed Sheeran and Arijit Singh Aziz Ansari’s Hollywood comedy ‘Good Fortune’
Aziz Ansari’s Hollywood comedy ‘Good Fortune’ Punjabi cinema’s power-packed star cast returns in ‘Sarbala Ji’
Punjabi cinema’s power-packed star cast returns in ‘Sarbala Ji’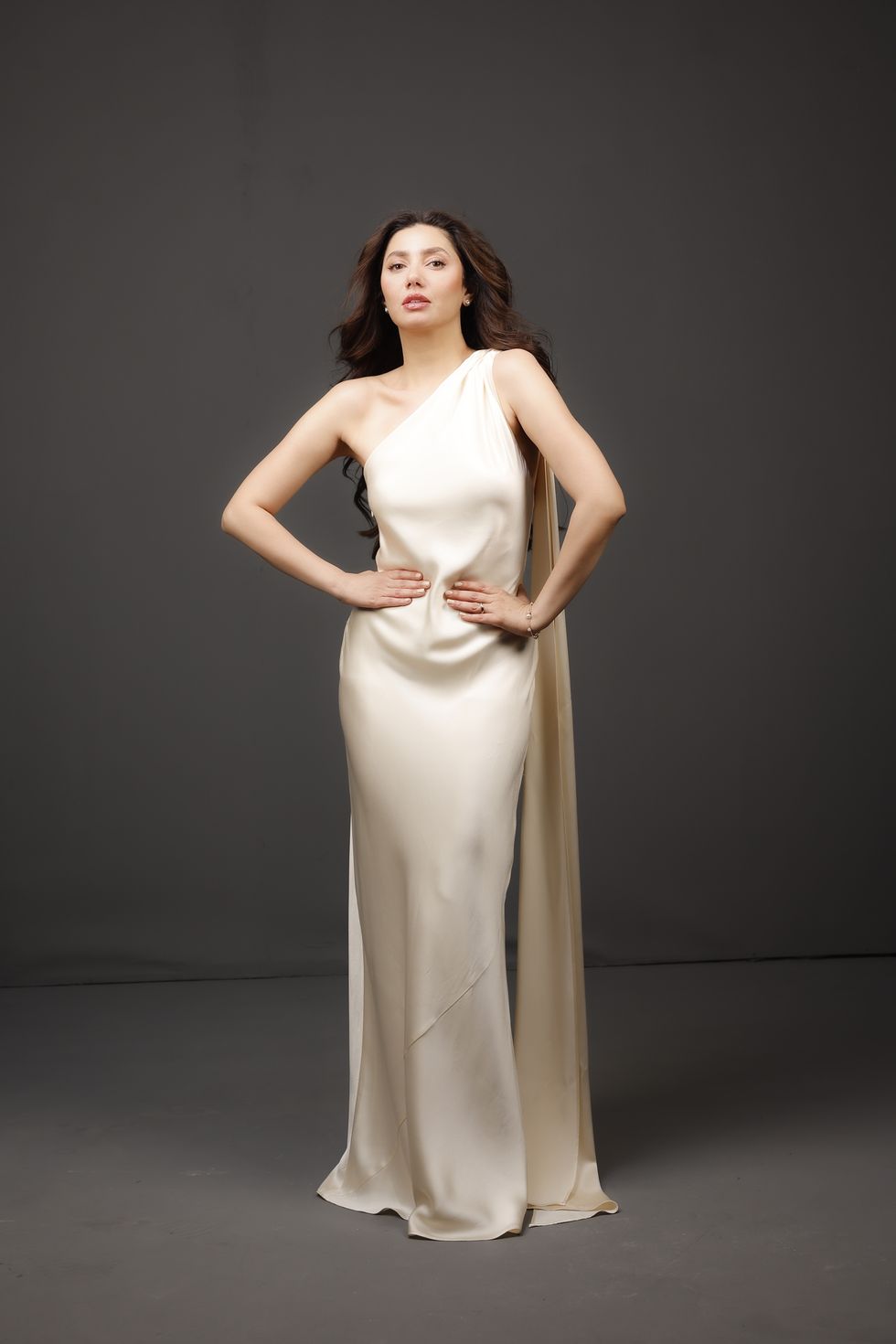 Mahira Khan
Mahira Khan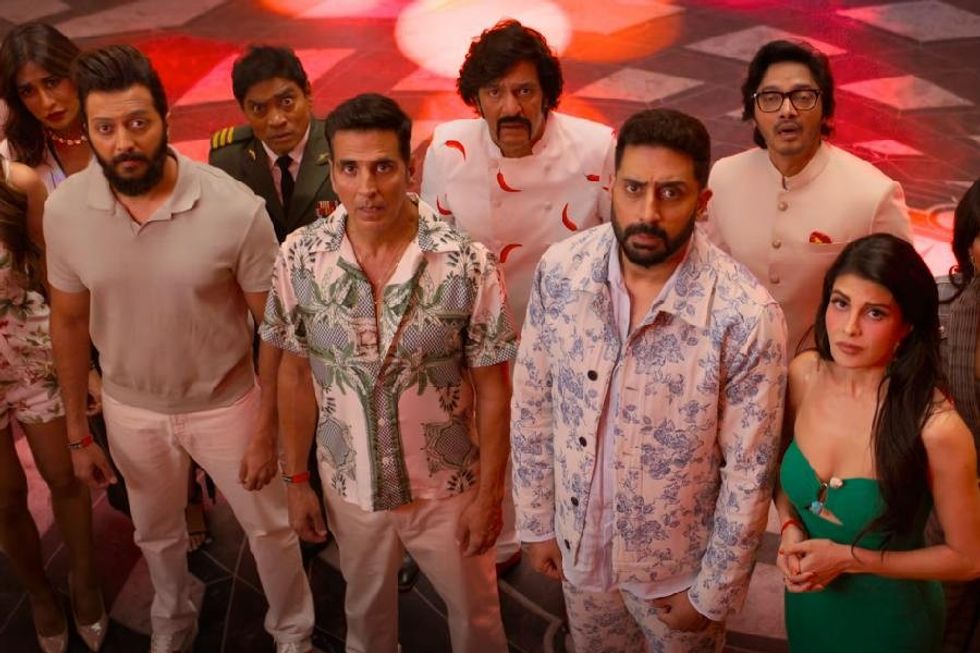 ‘Housefull 5’ proves Bollywood is trolling its own audience
‘Housefull 5’ proves Bollywood is trolling its own audience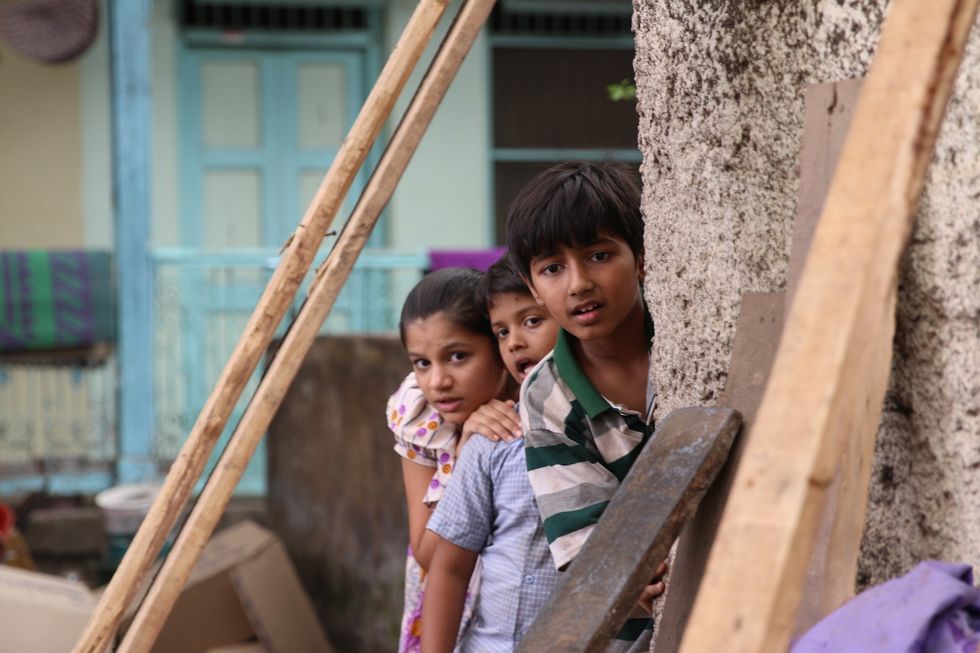 Brilliant indie film ‘Chidiya’
Brilliant indie film ‘Chidiya’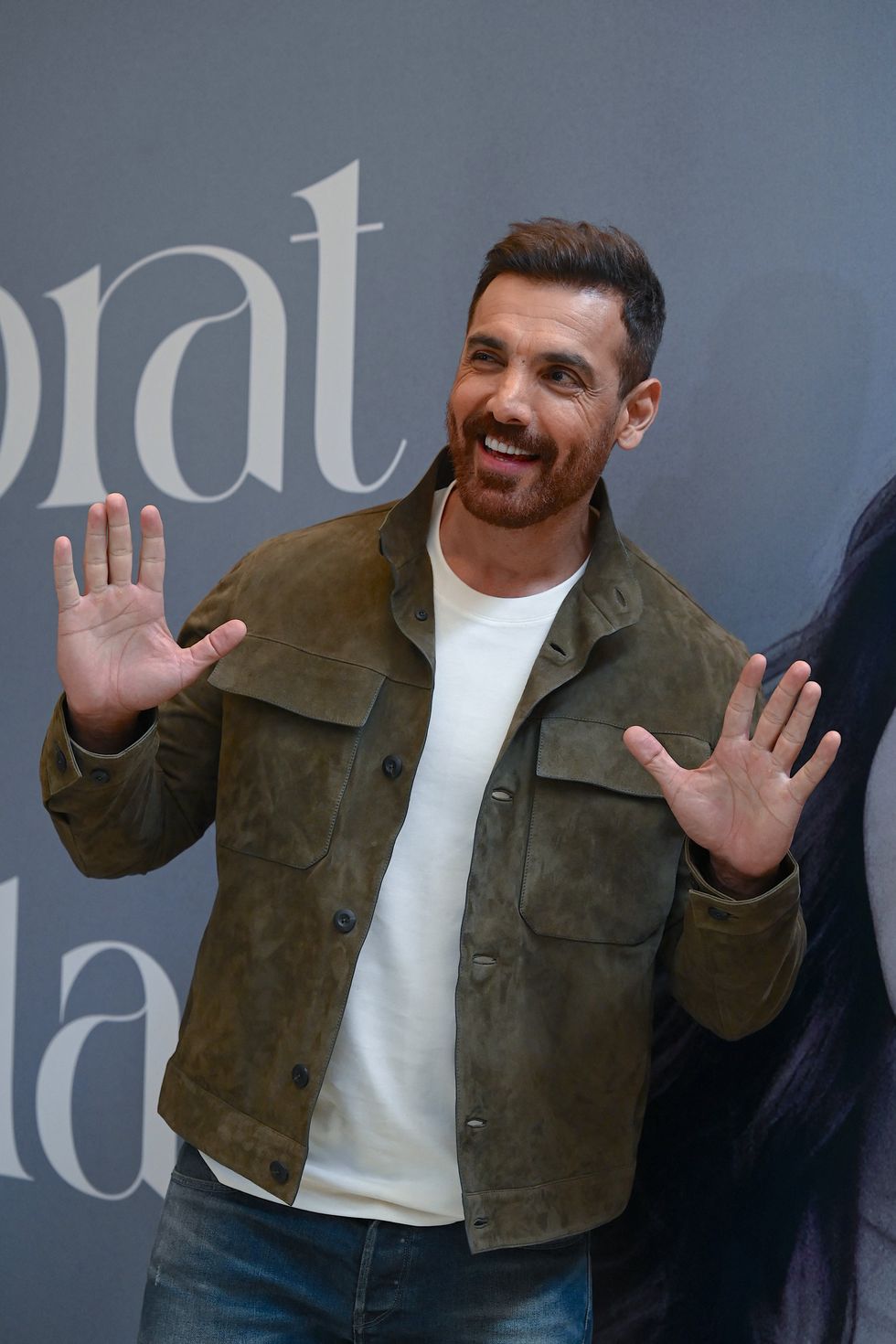  John Abraham
John Abraham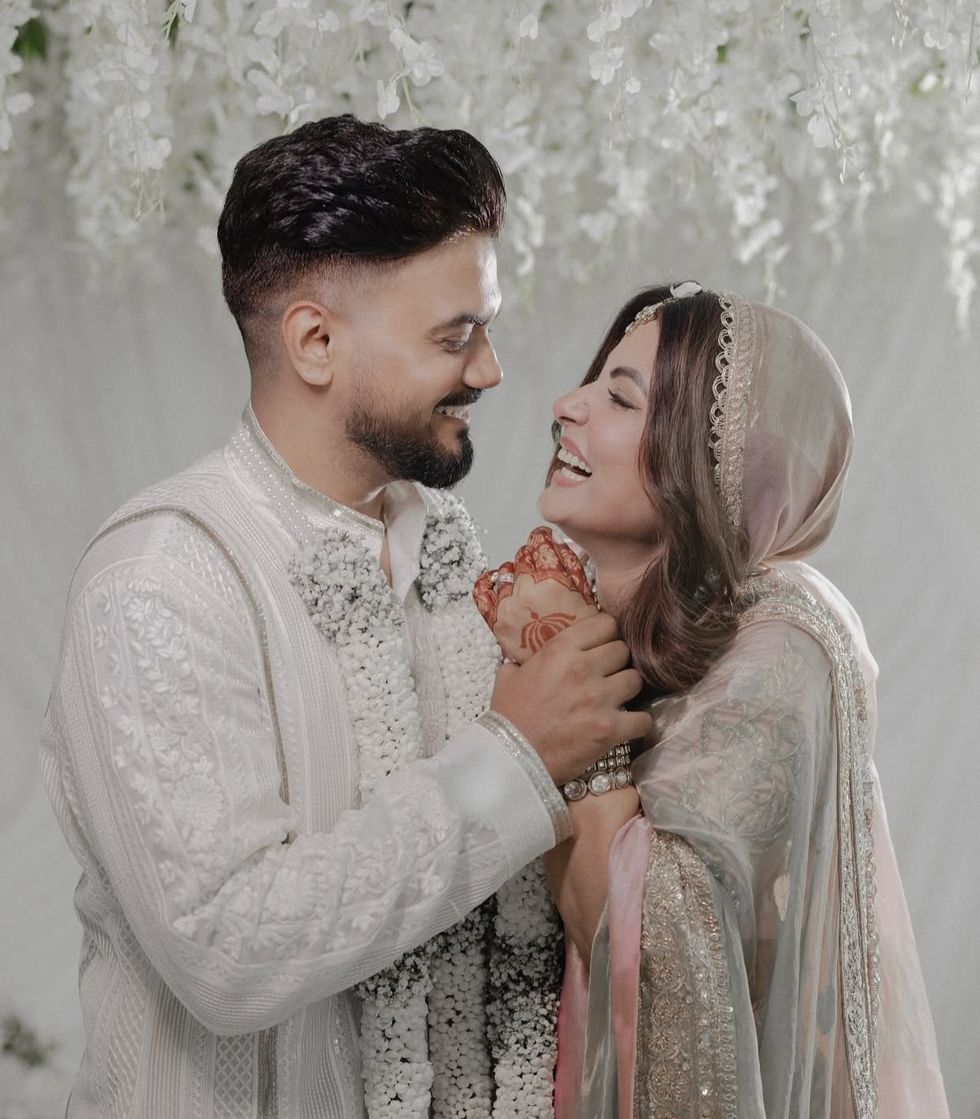 Hina Khan and her long-term partner Rocky Jaiswal
Hina Khan and her long-term partner Rocky Jaiswal  Shanaya Kapoor's troubled debut
Shanaya Kapoor's troubled debut Sana Yousuf
Sana Yousuf