Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. While some risk factors are well-established, such as diet and lifestyle choices, the exact causes of colon cancer are complex and not fully understood.
A recent groundbreaking study published in the journal Nature has shed light on a potential new player in this equation: a common mouth bacterium called Fusobacterium nucleatum.
The study, conducted by researchers at the Fred Hutch Cancer Center in the US, revealed a surprising link between a specific subtype of Fusobacterium nucleatum and the presence and progression of colon cancer. This bacterium, commonly found in the mouth, was detected within the tumours of roughly half of the 200 colon cancer patients examined.
Notably, the presence of this bacteria was associated with poorer patient outcomes, suggesting a potential role in promoting cancer growth and hindering treatment efficacy.
The researchers, led by co-corresponding author Susan Bullman, delved deeper to understand the mechanism behind this connection. Fusobacterium nucleatum is not typically found in the colon, raising the question of how it migrates from its usual habitat in the mouth to the distant location of the lower gut.
The study revealed a key finding: the specific subtype identified within the tumours, designated Fna C2, possessed distinct genetic variations compared to its mouth-dwelling counterparts. These variations suggest an adaptation for survival within the harsh acidic environment of the stomach, allowing the bacteria to make the journey from mouth to colon.
Further investigation revealed a higher prevalence of Fna C2 in stool samples of colon cancer patients compared to healthy individuals. This suggests that the bacteria not only manages to establish itself within the colon but also potentially contributes to the development of the cancerous environment.
The exact mechanisms by which Fna C2 promotes colon cancer growth remain under investigation. However, some theories have emerged. The bacteria may produce enzymes that damage host cells, creating a pro-inflammatory environment conducive to tumour formation. Additionally, Fna C2 could potentially shield cancer cells from the effects of chemotherapy drugs, leading to poorer treatment outcomes.
The implications of this research are significant. Identifying Fna C2 as a potential culprit in colon cancer development opens new avenues for treatment strategies. Therapies targeting this specific bacterial strain or its interactions with cancer cells could be explored. Additionally, the presence of Fna C2 in stool samples offers the potential for a non-invasive screening method for early detection of colon cancer.
Beyond the immediate findings, this research talks about the complex interplay between the human microbiome and various diseases. The human body harbours trillions of microorganisms, and their role in health and disease is becoming increasingly recognised. Understanding how specific microbes like Fna C2 interact with our systems offers valuable insights for preventative and therapeutic approaches.
However, further research is necessary to solidify these findings. Larger clinical studies are needed to confirm the association between Fna C2 and colon cancer across diverse populations. Additionally, a deeper understanding of the mechanisms employed by Fna C2 to promote cancer growth is crucial for developing targeted therapies.
The discovery of a link between Fusobacterium nucleatum and colon cancer is a significant step forward in our understanding of this complex disease.
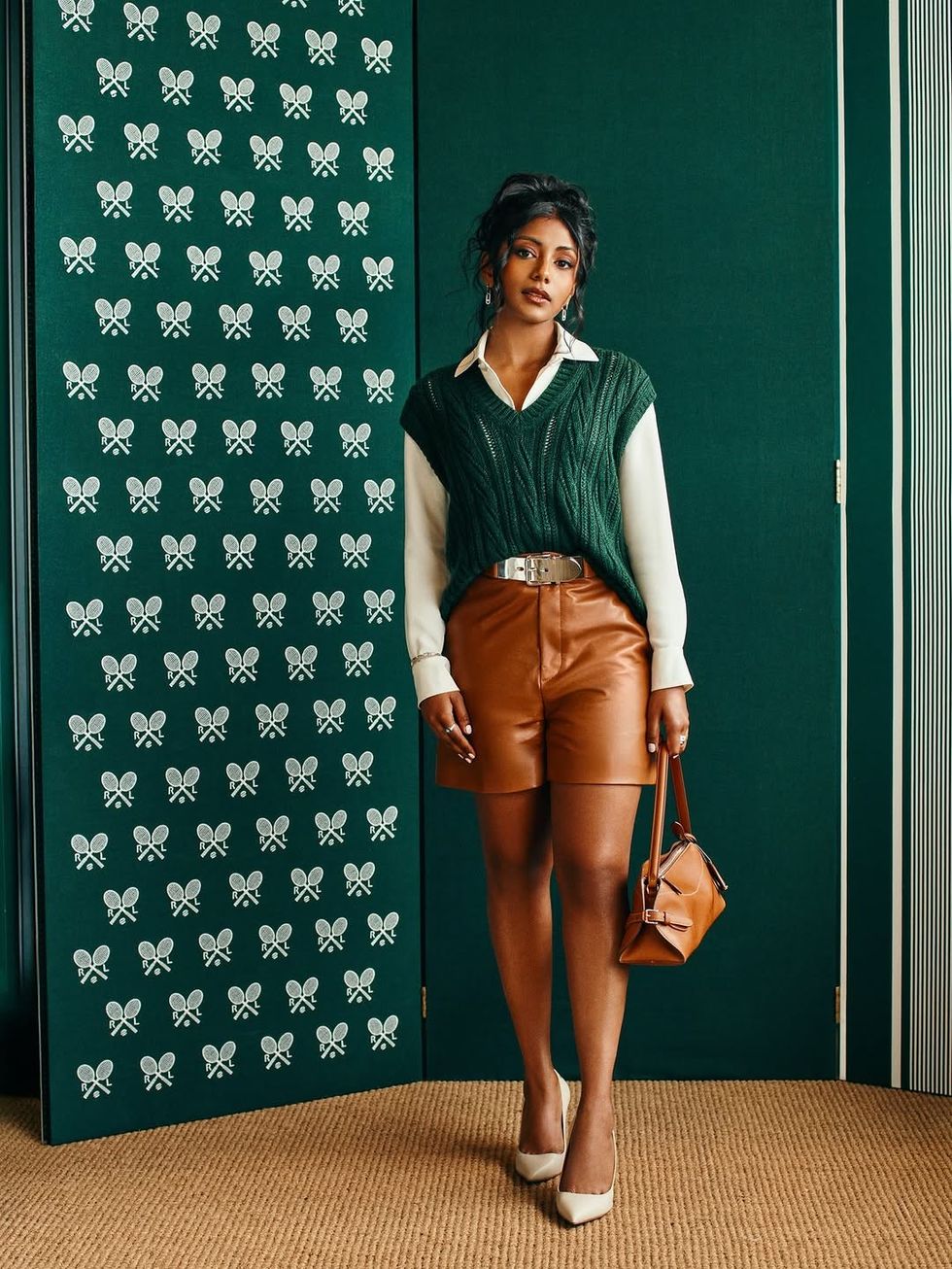














 Charithra Chandran styled her hair in soft curls for the Ralph Lauren outfitInstagram/
Charithra Chandran styled her hair in soft curls for the Ralph Lauren outfitInstagram/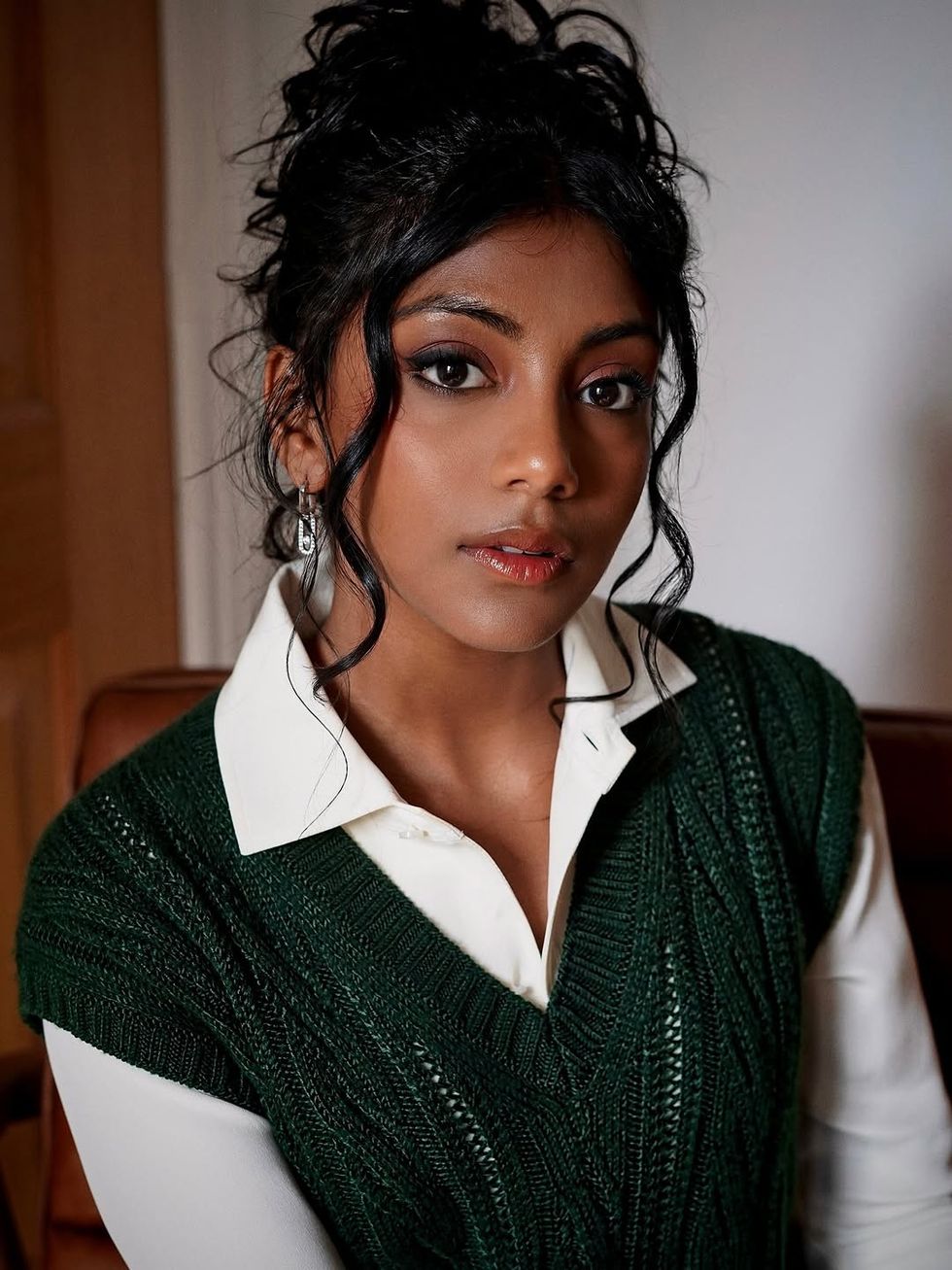 Charithra’s look was inspired by her character Edwina Sharma from BridgertonInstagram/
Charithra’s look was inspired by her character Edwina Sharma from BridgertonInstagram/

