INDIAN luxury goods from Bengal and Gujarat sourced by British businessmen were shipped to Africa, where they were bartered for slaves who were then transported to the colonies in America, a horrifying report by Historic England has revealed.
The report has sparked a furious reaction from right-wing lobbies angry that Historic England is “disturbing the accepted narrative” that heroes such as William Wilberforce led the world in ending Britain’s involvement in the slave trade with an Act of Parliament in 1807.
Like the National Trust, which came under attack for revealing that nearly 100 of the properties it looks after were built with the proceeds of either colonial loot in India or the slave trade, Historic England, too, is being pilloried by right-wing groups.
What is ironic perhaps is Historic England is not packed with “woke Lefties” but is an establishment organisation which receives £88.5 million from the government for “conserving historic buildings and other heritage sites”.
An unnamed source at the Department for Culture, Media and Sport was quoted as saying: “Ministers are increasingly frustrated with public bodies focusing on divisive parts of Britain’s history, rather than celebrating our shared heritage.”
Ministers – again unnamed – have apparently “accused Historic England of ‘putting down’ Britain’s past after the public body linked villages, halls, churches and pubs to slavery in a 157-page report”.
In fact, the report sets out in forensic detail how the huge sums made from the slave trade percolated down the generations and is responsible for much of the wealth of this country.
It shows how goods from India were swapped for African slaves. It states that “Erith (historically in Kent) was a busy port on the south bank of the Thames in the 18th century, importing goods from Britain’s new colonies, such as spices, textiles and tea.
“Many trading ships that transported goods there were part of the East India Company. These were then shipped to the West African coast and sold to merchants as barter for enslaved people.”
The modus operandi is explained: “The East India Company (set up in 1600) was a charted monopoly controlling trade with India, East and Southeast Asia, and was enormously influential... some of the goods traded in the transatlantic slave economy came from India.”
“The history of transatlantic slavery is indivisible from the history of England,” it points out.
“Recent events associated with the Black Lives Matter movement serve as a potent reminder of how this history of exploiting human life for profit permeates many aspects of English history.
“England’s role in the transatlantic slavery economy was part of a highly lucrative network of global commerce existing in Britain, West Africa, Virginia and other slave-holding British colonies in North America, and British territories in the Caribbean. It was a key component of Britain’s transformation into a world power in the 17th and 18th centuries.
“At its core was the exploitation of enslaved people of African descent to maximise profits from the plantation economies, resulting in material benefit for British colonial and metropolitan societies.”
The slave trade created a lucrative supply chain.
“Goods produced which were used directly in the transatlantic slave trade included shipbuilders, joiners and master craftsmen, sail makers, rope-makers and metal-workers making chains, manacles and other restraints used on slave ships,” the report says.
“The metal industries, for example, produced chains, padlocks, fetters, copper to sheath the slave ships, firearms and goods to exchange for captive Africans, alongside many of the tools used on slave plantations.
“Garments made with English wool became important trade items in the slave economies, as items to export to Africa, but also as direct exports to the plantations in the Americas as cheap durable woollens to clothe enslaved workers.”
The Transatlantic Slave Economy and England’s Built Economy: A Research Audit was commissioned by Historic England.
It has been written by academics Dr Mary Wills, honorary fellow, Wilberforce Institute for the Study of Slavery and Emancipation, University of Hull; and Dr Madge Dresser, associate professor in social and cultural British history at the University of the West of England.
They said: “Piecing together the connections between England’s colonial past and its industrial history, its public buildings or grand houses is a relatively new field of historical enquiry. For example, taking on the tangled web of familial connections that make up the history of English landed estates is one challenge to discovering how deeply England’s relationship with slavery is interwoven with this history.”
Their report states: “The Slave Voyages databases allow searches on nearly 36,000 slave voyages that occurred between 1514 and 1866, including those sailing from English ports.
“Cheap labour was central to the economic prosperity of the plantations. The British government encouraged transatlantic slavery on a large scale through the provision of royal charters to trading companies.
“The largest was the Royal African Company (RAC), set up by the Stuart family (on the throne from 1660) and London merchants, successor to an earlier monopoly, the Company of Royal Adventurers Trading to Africa.
“Slave ships departed English ports for trading posts on the west African coast taking a variety of goods to be exchanged for enslaved African people sold by African and European traders.
“Those held captive had invariably been kidnapped in the African interior or were prisoners of war. They endured a gruelling, often deadly, ‘Middle Passage’ across the Atlantic Ocean to the Americas, where they were purchased from ship captains by slave factors at an arranged price and resold at a profit to plantation owners in the Caribbean islands and North American colonies such as Virginia and South Carolina.
“The numbers of people enslaved in the transatlantic slave economy are extraordinary. Between 1501 and 1866, over 12 million Africans are estimated to have been exported to the Americas, around two million of whom did not survive the Atlantic crossing. British ships carried an estimated 3.25 million enslaved Africans between 1550 and 1807.”
When slavery was abolished, “compensation” was paid to those in Britain who had lost their “property”. Money from the slave trade was invested in homes and landscaping gardens. “Pineapples featuring as stone ornaments or on balustrades were modelled on pineapples cultivated on slave plantations, symbolising wealth, luxury and exoticism.”
Also, “family portraits often depicted black servants in the margins as a symbol of the family’s high status. Indeed, the African diaspora in England is one of the most obvious legacies of transatlantic slavery.
“Many people of African descent were brought from the West Indies and America with their owners (planters, sailors or military men) to become domestic servants, or acquired by wealthy families as a conspicuous sign of wealth and status. They served as pages, valets, footmen, coachmen, cooks and maids.”
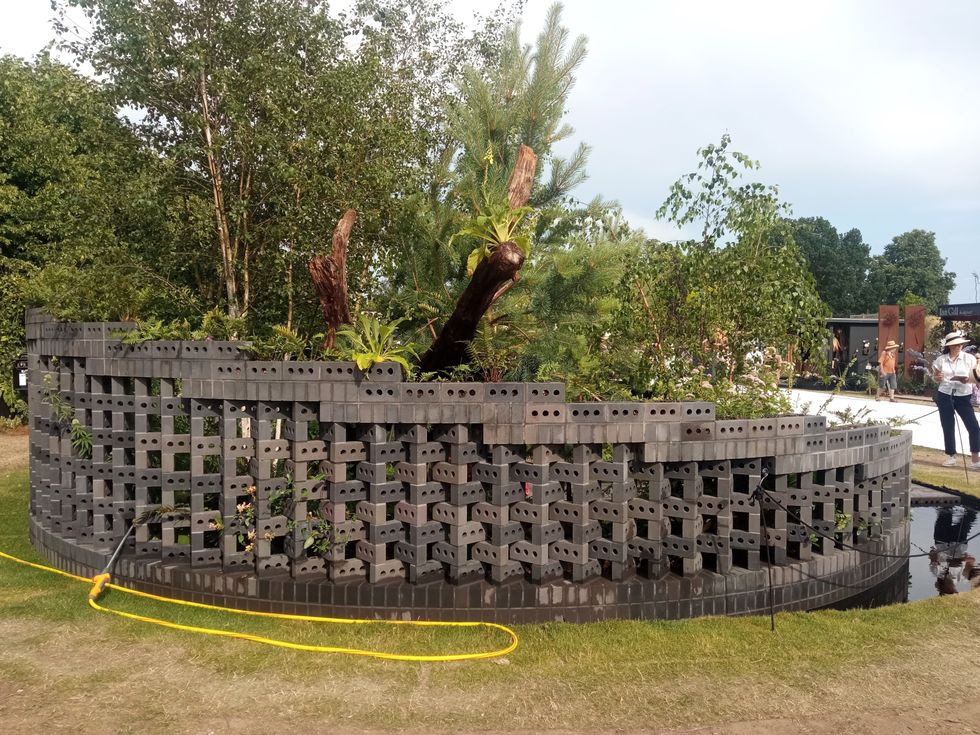





 The circular structure inspired by jali screens in India
The circular structure inspired by jali screens in India Sophie, Duchess of Edinburgh, at the garden
Sophie, Duchess of Edinburgh, at the garden The couple display their medals
The couple display their medals











 Kap’s Cafe in Surrey was struck by gunfire late at night with staff still insideInstagram/
Kap’s Cafe in Surrey was struck by gunfire late at night with staff still insideInstagram/ Kaps Cafe Instagram Story Instagram Screengrab/
Kaps Cafe Instagram Story Instagram Screengrab/ Kaps Cafe Instagram Story Instagram Screengrab/
Kaps Cafe Instagram Story Instagram Screengrab/
