RESEARCHERS in Nepal warned that the highest glacier on the top of Mount Everest could disappear by the middle of this century as the 2,000-year-old ice cap is thinning at an alarming rate.
The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) said that Everest has been losing ice significantly since the late 1990s, citing the latest research report.
The Everest Expedition, the single most comprehensive scientific expedition to Everest, conducted trailblazing research on glaciers and the alpine environment, the ICIMOD said.
The multidisciplinary team comprised scientists from eight countries, including 17 from Nepal. Three of the co-authors of the study were affiliated with the ICIMOD.
It has been estimated that the ice in the South Cole glacier located at an elevation of 8,020 metres is thinning at a rate of nearly two-mitre per year, the report said.
The findings were based on data from a 10-metre-long ice core obtained from South Col Glacier (in the Nepalese side of Everest) at an elevation of 8,020 metre and meteorological observations from the two highest automatic weather stations in the world located on the southern slopes of Everest at 7,945 and 8,430 metre.
The researchers, on the basis of radiocarbon dating, estimated the age of ice in the glacier to be 2,000-year-old.
The rate of ice loss measured is more than 80 times faster than the 2,000 years it took to attain this thickness.
"The long-term effect on the availability and stability of these water towers which will impact downstream communities is of major concern," the ICIMOD said in the statement.
Glaciers in the Himalayas make a significant contribution to water resources for millions of people.
The research finding states that the change in ice cover in the Everest could have been triggered by climate change.
In December 2020, China and Nepal announced that the world's highest peak is now taller by 86 centimetres after they remeasured Everest at 8,848.86 metres, over six decades after India conducted the previous measurement in 1954.
The revised height of Everest put an end to the decades-long dispute between the two neighbours on the height of the world's tallest mountain that straddles their shared border.
The exact height of Mt Everest had been contested ever since a group of British surveyors in India declared the height of Peak XV, as it was initially called, to be 8,778 metres in 1847.
Everest is known as Sagarmatha in Nepal while in China it is called Mt Qomolangma, the Tibetan name for the world's highest peak.
(PTI)
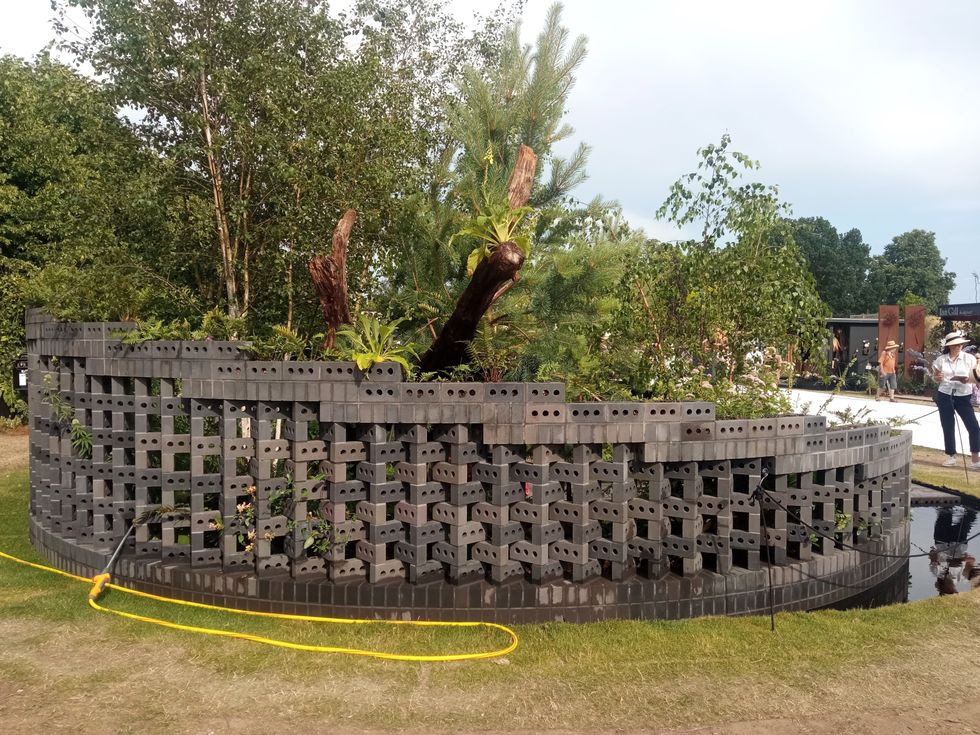
















 The circular structure inspired by jali screens in India
The circular structure inspired by jali screens in India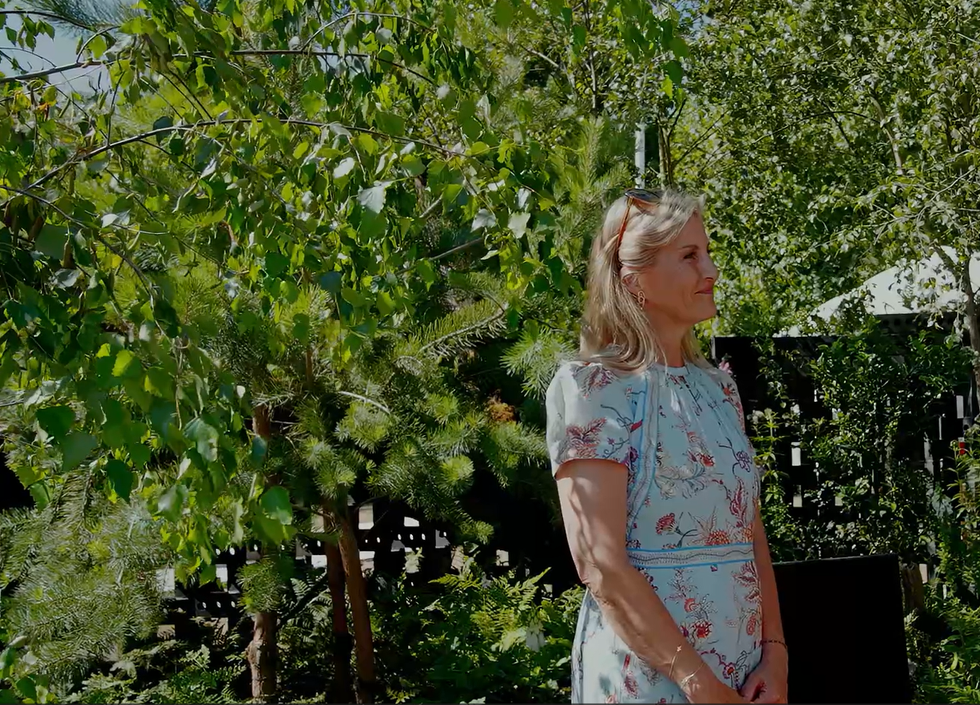 Sophie, Duchess of Edinburgh, at the garden
Sophie, Duchess of Edinburgh, at the garden The couple display their medals
The couple display their medals
