WHETHER it is multiple Hollywood remakes, including one headlined by Lady Gaga, Bollywood musicals like Aashiqui 2 and many others globally, a lot of movies have been inspired by 1937 classic A Star Is Born.
One of the finest is Hindi film classic Abhimaan, which was released on July 27 1973 and celebrates its 50th anniversary this week. The great story of a star mentoring a protégé and it leading to problems remains a great moment in Hindi cinema history.
Eastern Eye decided to mark 50 years of Abhimaan, by presenting reasons why it is a fantastic film.
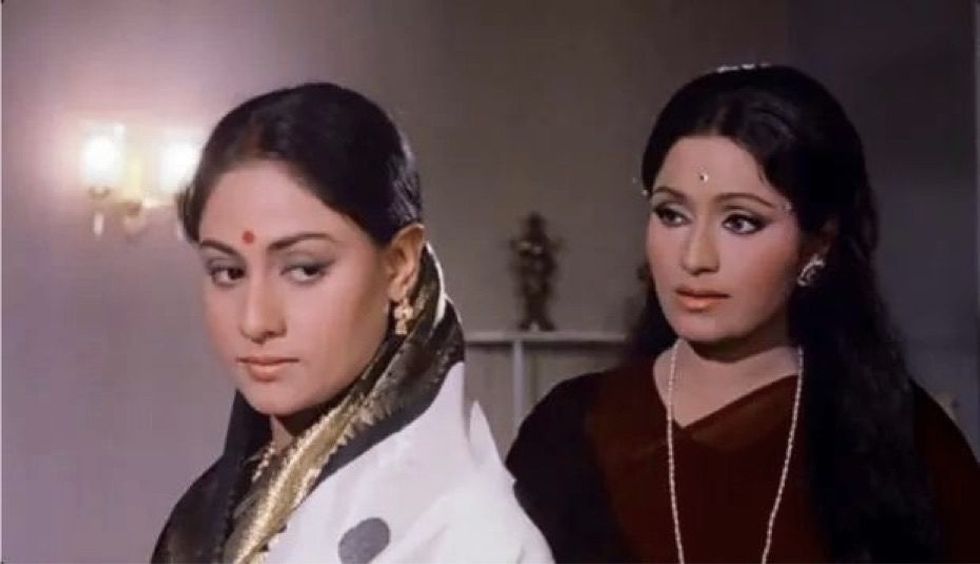
Empowerment: Despite the presence of a strong male character, the story celebrated the woman, and taught audiences to respect women and encourage them to grow. David’s character at the end even addresses the audience as beheno aur bhaiyo, instead of the usual bhaiyo aur beheno. Other women-centric films, namely Mother India, Kahaani, Khoon Bhari Maang, and Pakeezah, etc., largely relied on the absence of heroes. This wasn’t the case with Abhimaan. It also has a strong feminist message.
Mirror: This is the only version of this story where there would be an off screen connection to the lead couple, and that too in an opposite manner. Jaya Bhaduri was a bigger name when she met the relatively unknown Amitabh Bachchan, and the roles reversed when he went on to become Bollywood’s greatest star. For many it is their defining film together.
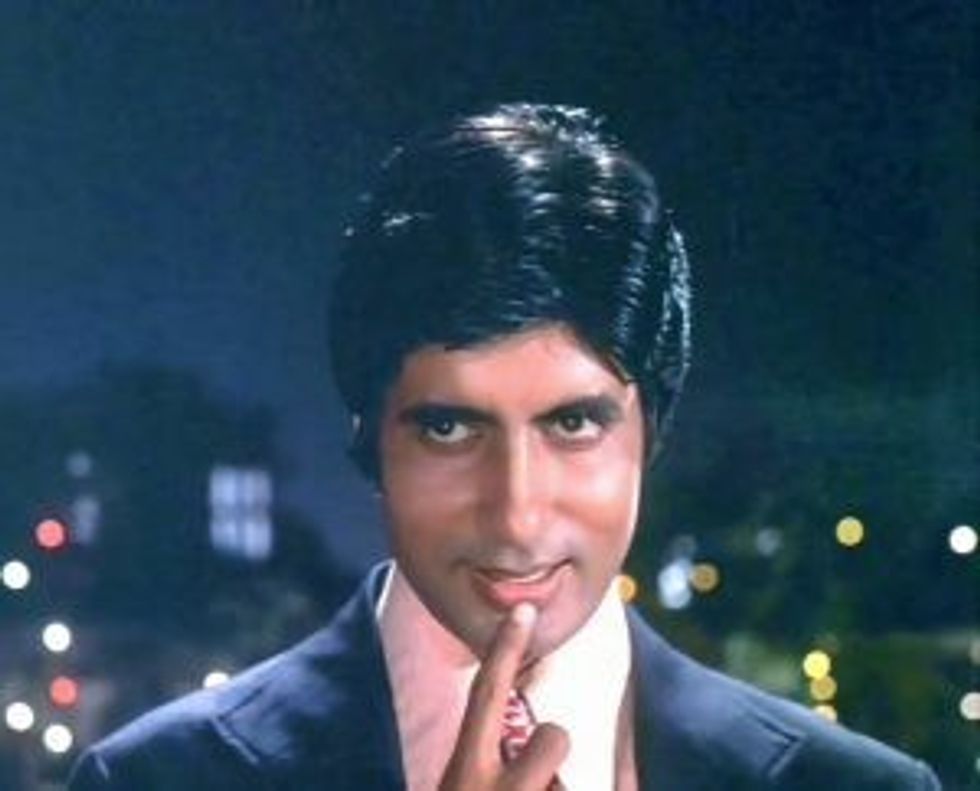
Acting: The lead stars delivered great performances, but what made this more interesting was that it was Bachchan’s last raw performance before superstardom kicked in and audiences started looking at him through a magnified lens.
Lessons: Abhimaan delivers many life lessons that remain relevant 50 years after it was released, including the perils of jealousy and ego, and the importance of humility. In one particularly poignant moment Bachchan’s character is told some home truths by Asrani, which really hit home. It is also seen as a movie that teaches working couples an important lesson.
Artistic: Most movies inspired by A Star Is Born are glitzy entertainers, but what director Hrishikesh Mukherjee brilliantly did was find the hallowed middle ground between the commercial and artistic with this film. It gave the movie added depth and realism.

Journey: Instead of the established star committing suicide like in the other films, the lead protagonist goes on a complete journey. In the opening he is seen as a confident celebrity on stage, dressed in western attire. The final scene is also on stage, but by now he has found humility, while his ego is shattered. He is apologetic and appears in traditional Indian clothes.
Songs: One of the last great soundtracks composed by legendary music director SD Burman has timeless songs, which found power in simplicity and remain wonderful 50 years later. With lovely lyrics by Majrooh Sultanpuri, the songs were a connecting point between the golden era of Hindi cinema and more modern music that came later. In many ways, the songs acted like the narrator of a powerful story. SD Burman would win a Filmfare Best Music Director award.
Music: The songs were entertaining, but Abhimaan also showed how much of a big part music plays in people’s lives, which other adaptations did not really do. The movie also showed the real talents and trained maestros as down to earth individuals, who loved the purity of music ahead of any fame, which is something not seen in other adaptations of A Star Is Born.
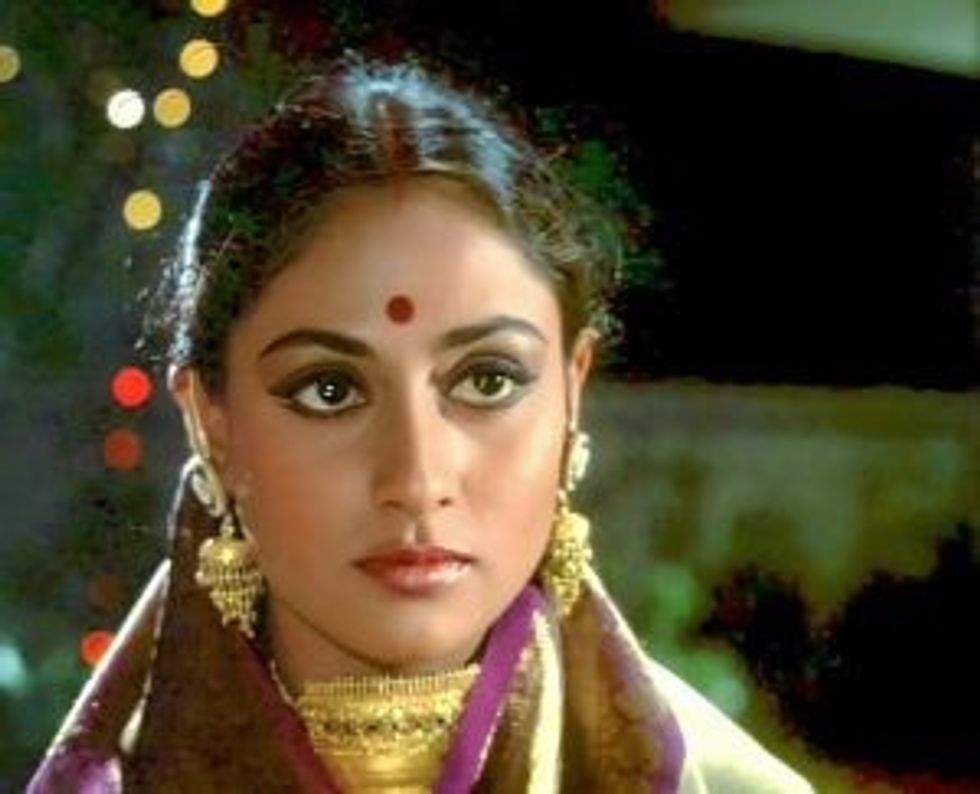
Nightingale: Lata Mangeshkar delivered some of the finest songs of her illustrious career in the film. In many ways the character played by Jaya Bhaduri represented her natural talent and simplicity.
Themes: The simple story skilfully tackles multiple themes that include toxic masculinity, ego, fragility of marriage, fleeting nature of fame, love, the relationship of an artist with fame, redemption, and mental health. It is also a cautionary tale of letting your own importance take over.
Reality: Abhimaan didn’t need the heroes and villains that have largely defined Hindi cinema. It has grey shaded characters rooted in reality, who are trapped in societal expectations, which is why it remains relevant and relatable 50 years later.
Simplicity: Whether it was the relatively simple setting, stripped back songs or understated performances, the musical drama showed that less could be more. That was largely due to the effective story, skilled direction, and great performances by the actors.
Flawed hero: When the movie was made, the Bollywood hero was nearly always a shining beacon of goodness, but Abhimaan flipped the script and made him flawed. This made him more relatable to audiences.
Ending: Pretty much all the remakes of A Star Is Born have a tragic ending with the
male protagonist giving into suicide, but in Abhimaan he learns an important lesson without resorting to drastic action and subsequently gives a more powerful message to audiences.
Scenes: Whether it is Bindu greeting the newlyweds with grace and dignity, musical moments, Bachchan’s character getting drunk, the confrontations, conflicts, and moments of remorse, Abhimaan is filled with memorable scenes.
Family friendly: It may have dealt with adult themes, but the movie was family friendly and ultimately connected with audiences of all ages across the decades. That is why it remains a classic today.
Did you know?
- Abhimaan released weeks after Amitabh Bachchan and Jaya Bhaduri had got married.
- It was the first film produced by Amitabh and Jaya under their company Amiya, with their personal secretaries fronting it.
- The film was initially titled Raag Ragini.
- Jaya Bhaduri won a Filmfare Best Actress award for her performance, which she jointly shared with Dimple Kapadia, for her role in Bobby.
- One historical account says the story was inspired by the break-up of Kishore Kumar and his wife Ruma Guha Thakurta. Another claims the story was inspired by the troubled marriage of classical Indian maestros Pandit Ravi Shankar and Annapurna Devi.
- Popular singer Anuradha Paudwal started her film journey by singing the song Omkaram Bindu Sanyuktam for Abhimaan.
- The film’s song Loote Koi Man Ka Nagar was supposed to be sung by Mukesh. But he refused after hearing the demo version by Manhar Udhas and said he should remain the singer.
- Asrani and Bindu got Best Supporting Actor and Actress nominations at the Filmfare Awards, for roles that were dramatically different to their usual comedian and vamp characters.
- Abhishek Bachchan wanted to remake Abhimaan with director Rakeysh Omprakash Mehra.
- The song Nadiya Kinaare was shot entirely in a tourist village called Asoga.



















 Naeli and the secret song
Naeli and the secret song
 Jamie Lloyd’s Evita with Rachel Zegler set for Broadway after London triumphInstagram/
Jamie Lloyd’s Evita with Rachel Zegler set for Broadway after London triumphInstagram/
 A compelling premise, layered and unpredictable charactersAMG
A compelling premise, layered and unpredictable charactersAMG Anyone who enjoys a gripping story with a diverse cast and unexpected twistsHarperFiction
Anyone who enjoys a gripping story with a diverse cast and unexpected twistsHarperFiction
 The Story Teller by Ley Roberts
The Story Teller by Ley Roberts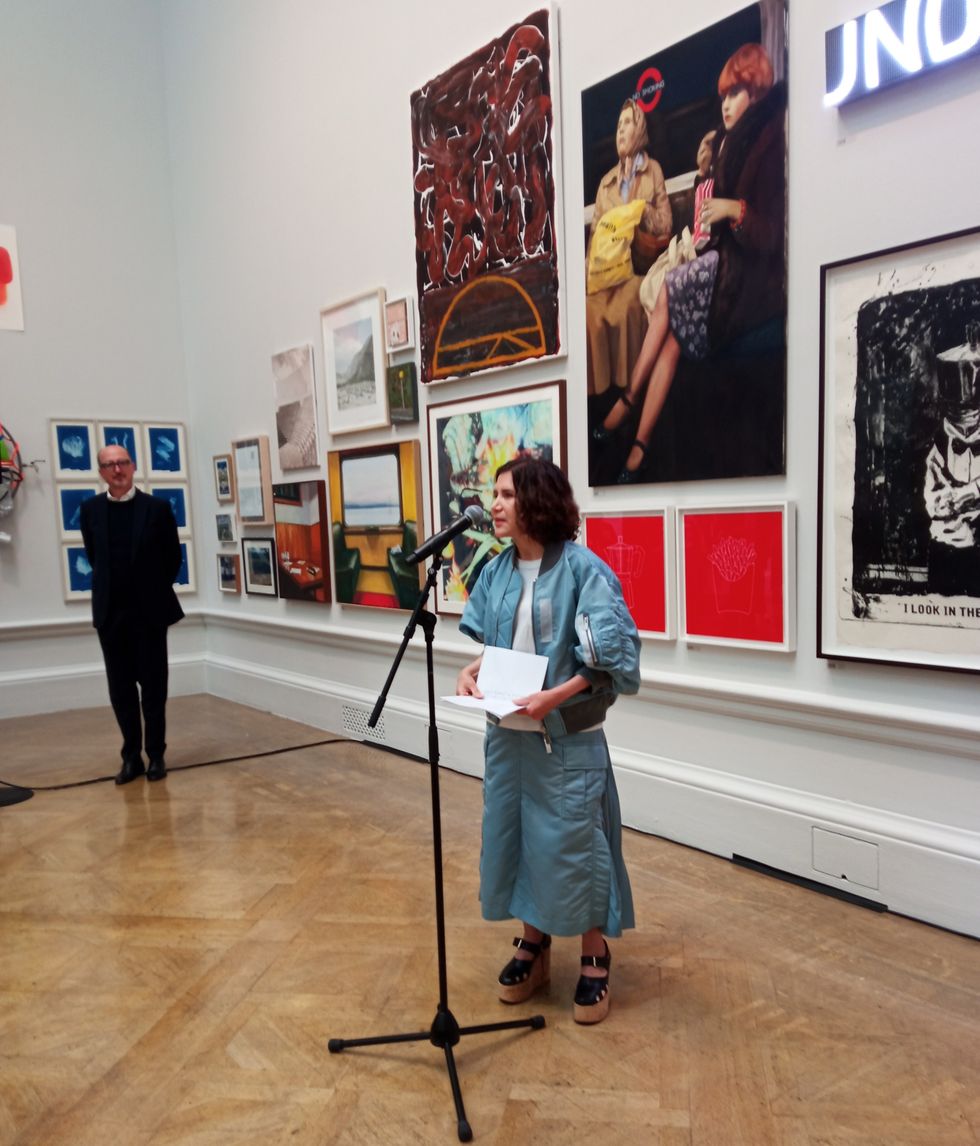 Summer Exhibition coordinator Farshid Moussavi, with Royal Academy director of exhibitions Andrea Tarsia in the background
Summer Exhibition coordinator Farshid Moussavi, with Royal Academy director of exhibitions Andrea Tarsia in the background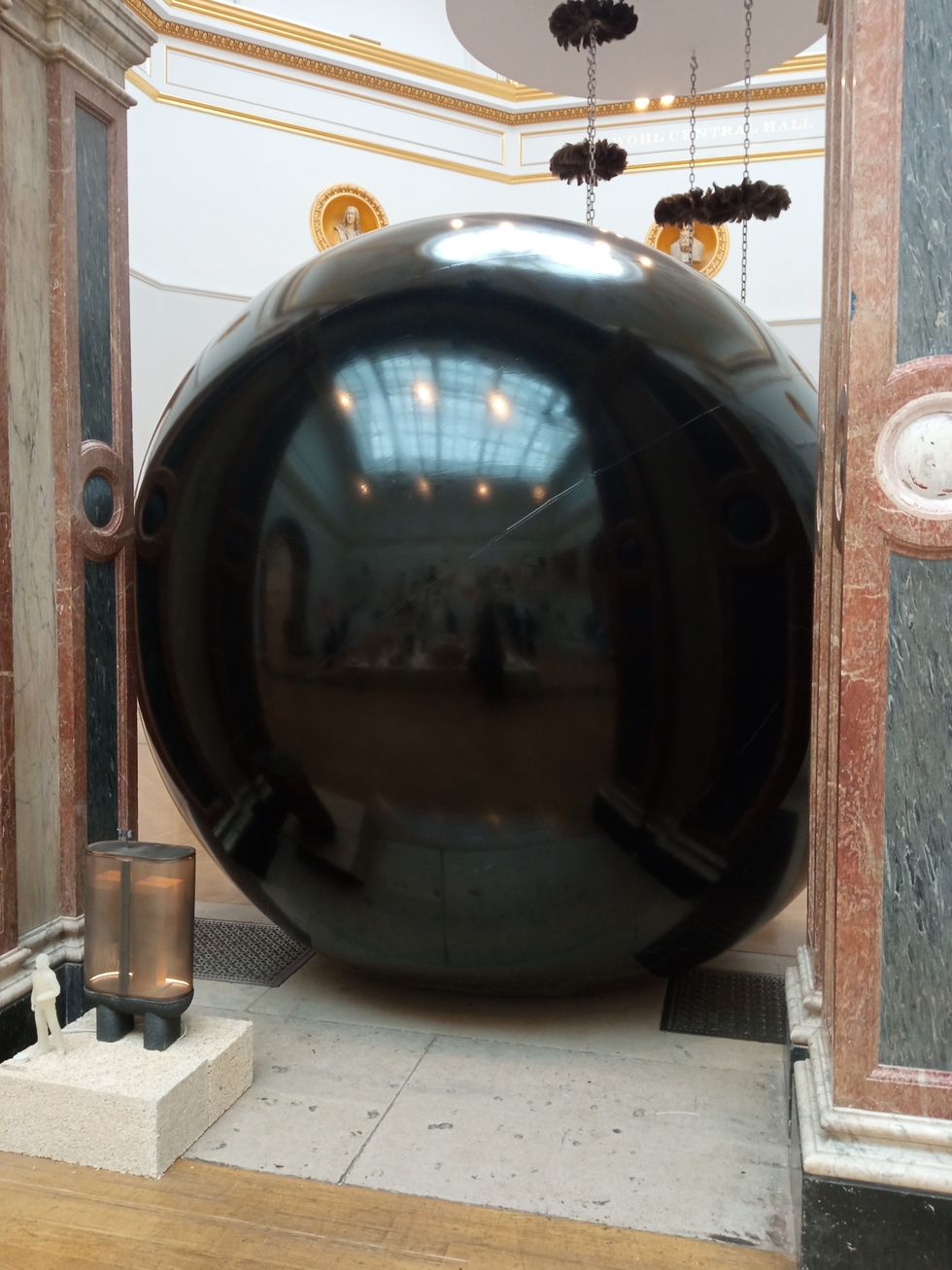 An installation by Ryan Gander
An installation by Ryan Gander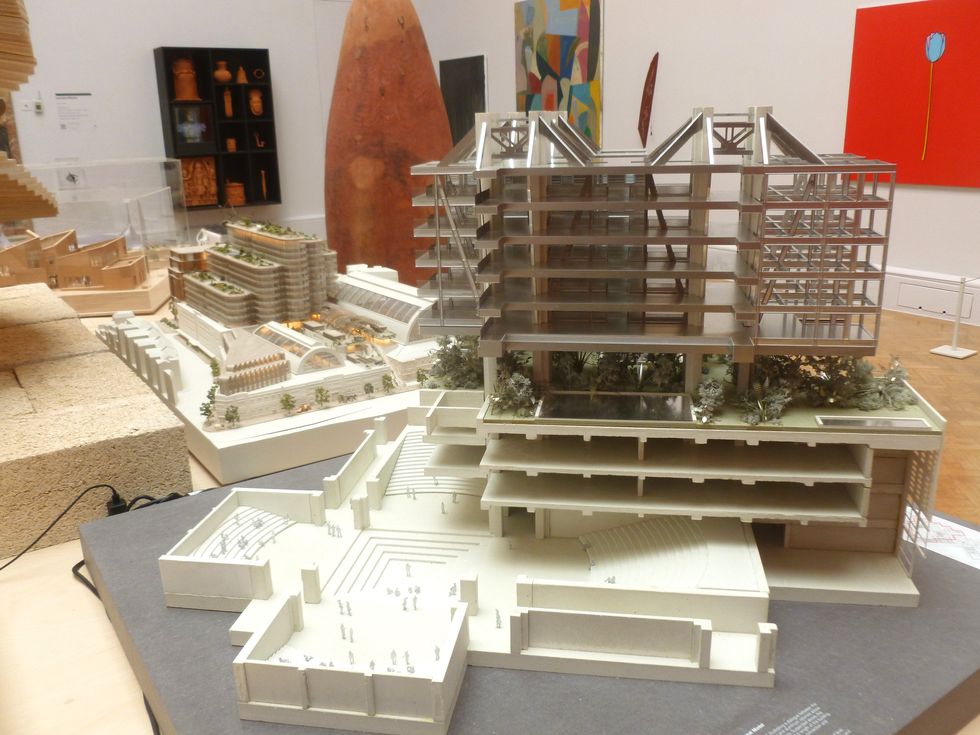 A sectional model of DY Patil University Centre of Excellence, Mumbai, by Spencer de Grey
A sectional model of DY Patil University Centre of Excellence, Mumbai, by Spencer de Grey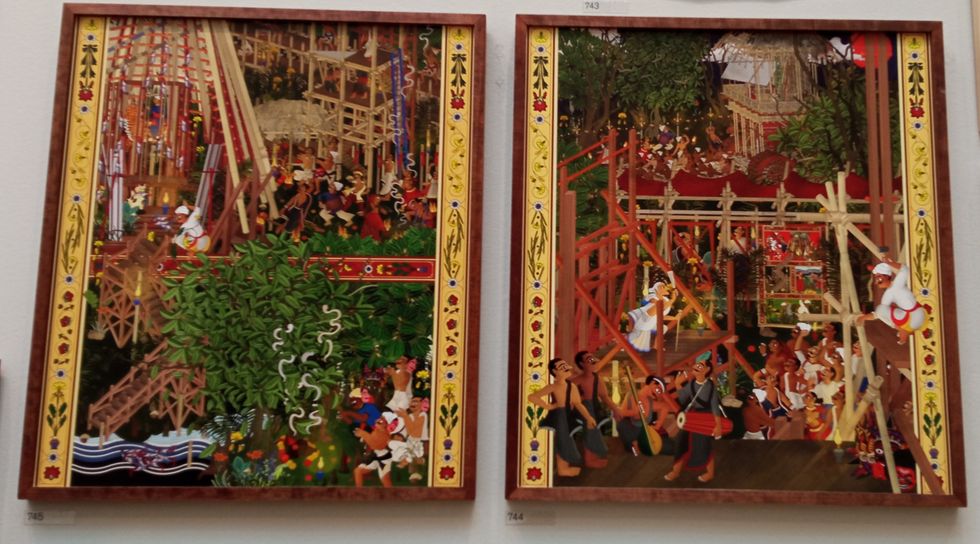 Rituals and Identity and Theatre of Resistance by Arinjoy Sen
Rituals and Identity and Theatre of Resistance by Arinjoy Sen