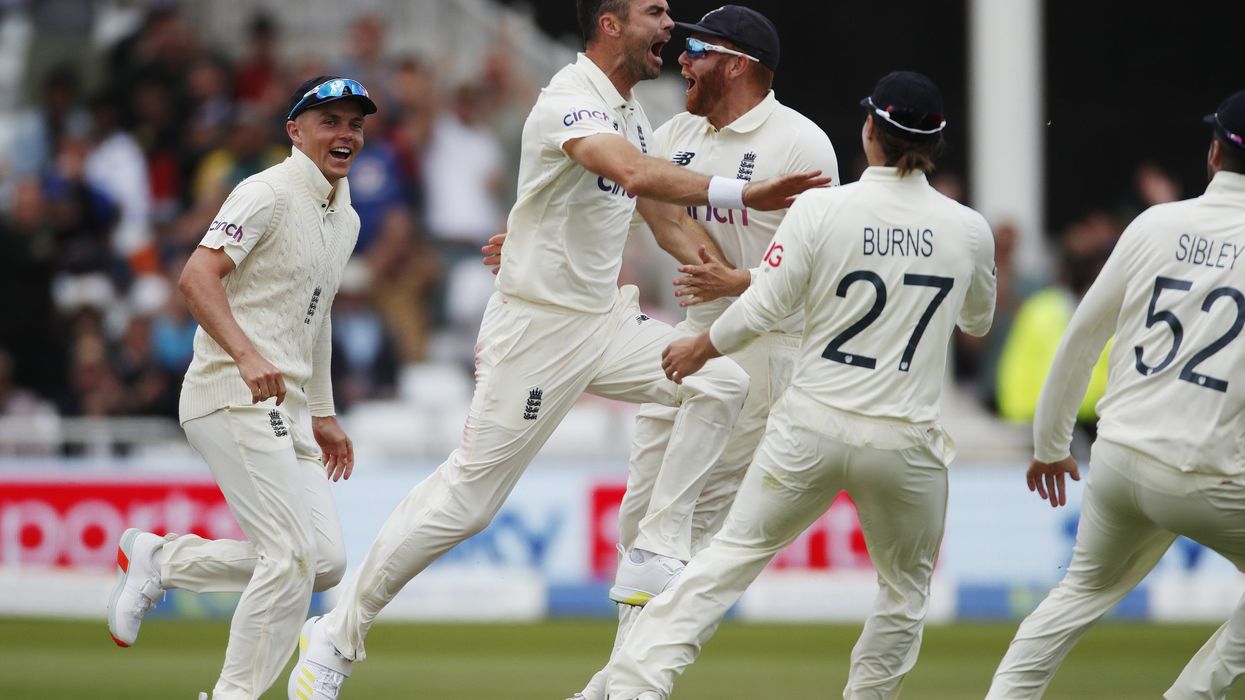
INDIA captain Virat Kohli was out for nought first ball in the first Test amid a collapse that saw England great James Anderson take two wickets with successive deliveries on Thursday's (5) second day at Trent Bridge.
Kohli was caught behind off Anderson by wicketkeeper Jos Buttler one ball after Cheteshwar Pujara fell to the same combination for four.
India had been in total command at 97 for 0 in reply to England's meagre first innings 183 but then lost four wickets for 15 runs either side of lunch as they slumped to 112 for 4.
The wickets were welcome news for England after it had been announced earlier on Thursday (5) that Jofra Archer, not playing in this match, would be ruled out for the rest of a year with a recurrence of an elbow injury, meaning the fast bowler would miss both the T20 World Cup and the Ashes tour of Australia.
By the time bad light and then rain combined to bring about an early finish to the day's play, India were 125 for 4 - a deficit of 58 runs.
Rahul shines
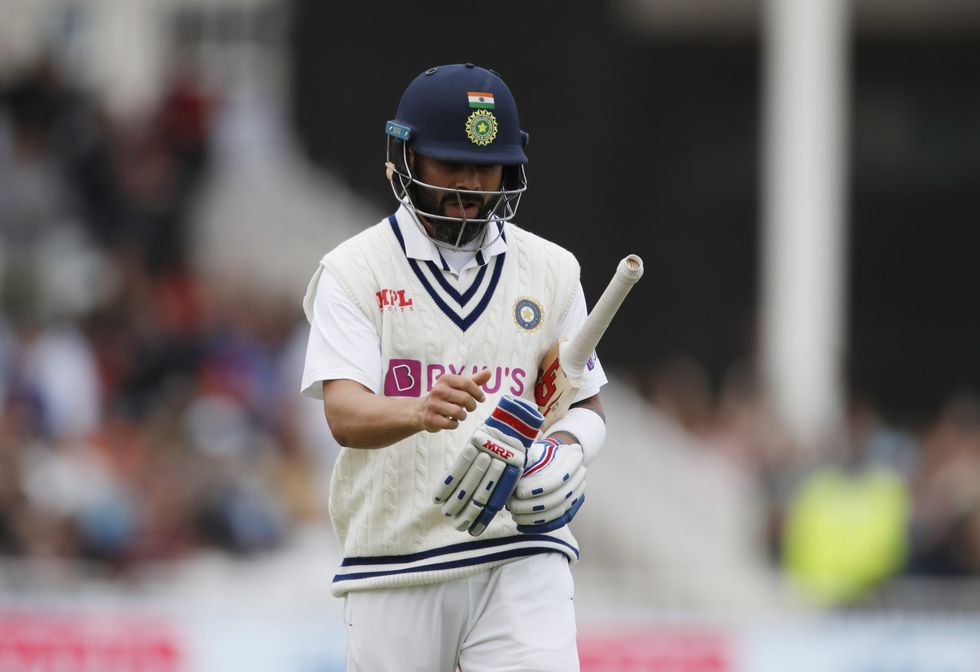
One consolation for India was that recalled opener KL Rahul was still there on 57 not out after being reprieved on 52 when Dom Sibley dropped a regulation slip catch. Rishabh Pant was unbeaten on seven.
Star batsman Kohli was undone by a brilliant Anderson delivery that lifted and moved late to take the edge on its way through to Buttler.
The ball before Anderson, previously wicketless in the innings, had number three Pujara caught low down by Buttler for four.
Ajinkya Rahane survived the hat-trick when Anderson strayed down the legside, but England's all-time leading Test wicket-taker still had figures of 2-15 in 13.4 overs at stumps.
Rahane, then the non-striker, was soon out for five in any event when, having been left stranded when Rahul set off and then stopped, he was run out by Jonny Bairstow's direct hit from backward point.
Rahul, having completed a 128-ball fifty including eight fours, ought to have been Anderson's third wicket of the day but Sibley floored a catch off an outside edge going to his left at second slip despite getting both hands to the ball.

Anderson started his 14th over but could only manage one ball before the umpires took the players off the field for bad light.
With rain falling, play did not resume again with Anderson then managing one more ball before a fresh shower.
The umpires got play going again with Anderson bowling two more balls only for a fresh burst of rain to halt play again, with two balls left in an over that had started more than two-and-a-half hours earlier.
India had been in command for all but one ball of the morning's play after resuming on 21-0.
Both Rahul, recalled after Mayank Agarwal was ruled out with suspected concussion when hit on the head batting in the nets on Monday - and Rohit Sharma blunted England's attack with disciplined skill.
But on the stroke of lunch, Sharma fell for 36 when, in what appeared to be a lapse in concentration, he pulled a surprise short ball from the Ollie Robinson to Sam Curran at fine leg.
India's four-man pace attack had performed superbly to dismiss England on Wednesday, with Jasprit Bumrah taking 4 for 46.
Only England captain Joe Root, who won the toss, with 64 passed 29 in an innings that featured four ducks - the third time this had happened to England in their last five Tests.
(AFP)