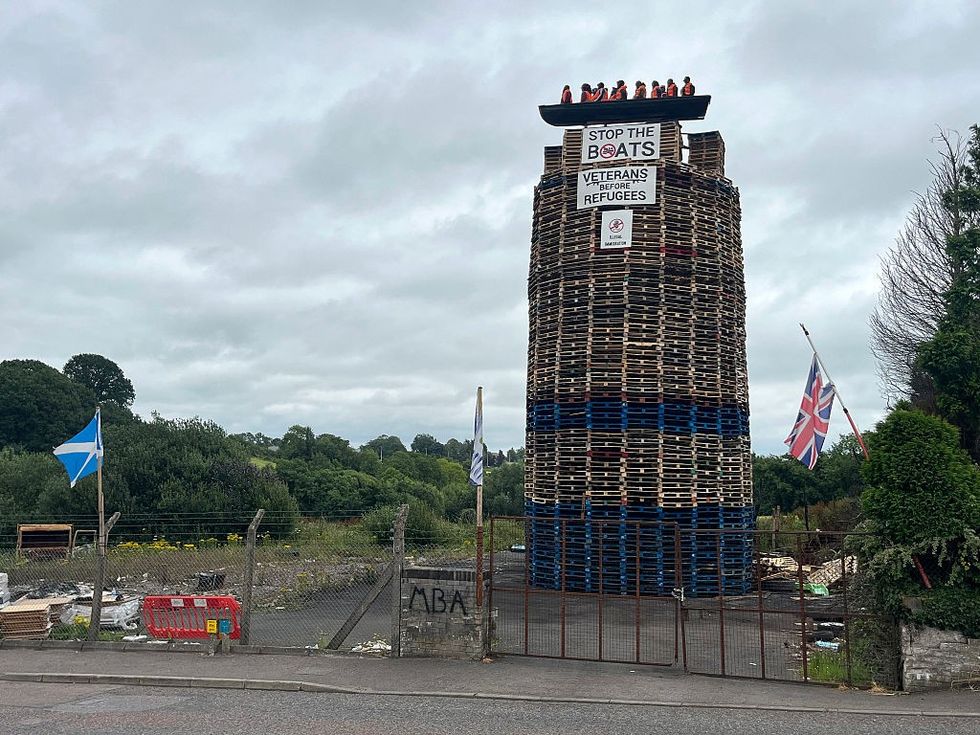
Addiction is a complex and insidious condition that can infiltrate lives without warning, leaving a trail of devastation in its wake. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), substance use disorders cost the United States more than $600 billion annually in healthcare costs, crime-related expenses, and lost productivity. Early identification of addiction is crucial in preventing its progression and mitigating its harmful consequences.
By recognizing the signs and taking proactive measures, individuals, families, and communities can intervene before addiction takes a firm hold. Here are ten strategies that can aid in the early identification of addiction.
Tips for Identifying Risk Factors for Addiction Early
Addiction is a multifaceted issue that can profoundly impact individuals' lives, relationships, and overall well-being. Recognizing addiction risk factors early can be a game-changer in preventing substance abuse and its devastating consequences.
With 80% of substance use disorders stemming from adolescence, early identification becomes a crucial intervention strategy for what is addiction. By proactively understanding and addressing these risks, we can enhance outcomes and guide individuals toward healthier lifestyles.
Here are some tips to help you recognize potential signs of addiction risk:
1. Emotional and Psychological Indicators
Pay close attention to changes in mood, behavior, and mental state, as these can often be early indicators of vulnerability to addiction. Some warning signs include:
- Persistent feelings of depression, anxiety, or low self-esteem
- Difficulty coping with stress or traumatic events
- Impulsivity or poor impulse control
- Difficulty regulating emotions
2. Behavioral Changes
Significant shifts in behavior can signal the onset of addictive tendencies. Be mindful of the following:
- Withdrawing from social activities or relationships
- Neglecting responsibilities or personal hygiene
- Sudden changes in academic or professional performance
- Engaging in risky or illegal behaviors
3. Substance Experimentation
While occasional substance use or experimenting with substances may not necessarily lead to addiction, it's essential to be mindful of patterns that could signal problematic behavior. Frequent or excessive use, combining different substances, and using substances as a coping mechanism are all red flags that should not be ignored. Pay attention to these patterns and address them promptly before they escalate.
4. Coping Mechanisms and Self-Regulation
Healthy coping mechanisms and self-regulation skills can act as protective factors against addiction. Be mindful of:
- Difficulty managing stress or emotions
- Lack of effective problem-solving skills
- Reliance on avoidance or escapism as coping strategies
By being aware of these risk factors, you can take proactive steps to address underlying issues, seek professional support, and implement preventive measures. Early intervention can significantly improve the chances of avoiding the devastating consequences of addiction and promoting overall well-being.
5. Understand the Risk Factors
Addiction doesn't discriminate; it can affect individuals from all walks of life. However, certain risk factors can increase an individual's vulnerability. Familiarizing yourself with these risk factors is an essential first step in recognizing potential addiction patterns.
Genetic predisposition, mental health conditions, trauma, and environmental influences can all contribute to the development of addictive behaviors.
6. Family History and Environmental Factors
Genetics and environmental influences can play a role in addiction susceptibility. Consider:
- A family history of addiction or mental health disorders
- Exposure to trauma, abuse, or neglect
- Peer pressure or social environments that encourage substance use
7. Implement Screening Tools
Professional screening tools, such as the CRAFFT questionnaire for adolescents or the AUDIT for adults, can be invaluable in identifying potential substance use disorders. These evidence-based assessments provide a structured approach to evaluating risk factors and guiding further intervention or treatment.
- The CRAFFT (Car, Relax, Alone, Forget, Friends, Trouble) is a widely used screening tool for adolescents, designed to detect high-risk substance use.
- The AUDIT (Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test) is a 10-item questionnaire developed by the World Health Organization to assess alcohol consumption, drinking behaviors, and alcohol-related problems.
- Regular screening, especially in high-risk populations or settings, can help identify potential issues before they escalate.
8. Foster Open Communication
Addiction thrives in secrecy and stigma. By fostering an environment of open communication, where individuals feel comfortable discussing their struggles without fear of judgment, you can create a supportive network that encourages early disclosure and help-seeking behavior.
- Encourage open and honest dialogue about substance use and mental health challenges.
- Provide a safe and non-judgmental space for individuals to share their experiences and concerns.
- Ensure confidentiality and respect for privacy to build trust and facilitate open communication.
9. Educate and Raise Awareness
Knowledge is power in the fight against addiction. Providing comprehensive education on the risks, signs, and consequences of addiction can empower individuals and communities to recognize potential issues early on. Awareness campaigns and educational programs can help destigmatize addiction and promote a culture of prevention.
- Implement educational initiatives in schools, workplaces, and community settings to raise awareness about addiction and its early warning signs.
- Leverage various mediums, such as workshops, seminars, online resources, and social media campaigns, to disseminate information effectively.
- Collaborate with healthcare professionals, addiction specialists, and community leaders to ensure accurate and credible information is shared.
10. Leverage Community Resources
Early identification efforts should not be limited to individual or family efforts alone. Leveraging community resources, such as support groups, counseling services, and addiction treatment centers, can provide a collaborative approach to identifying and addressing addiction risks. These resources can offer professional guidance, support, and evidence-based interventions.
- Establish partnerships with local addiction treatment centers, mental health clinics, and non-profit organizations to create a comprehensive support network.
- Promote the availability of community resources through outreach programs and awareness campaigns.
- Encourage individuals and families to utilize these resources for early intervention, support, and guidance.
Conclusion
Early identification of addiction is a critical step in preventing its devastating impact on individuals, families, and communities. By employing these strategies, we can foster a culture of awareness, support, and proactive intervention, empowering individuals to seek help and reclaim their lives before addiction takes hold.
Remember, addiction is a treatable condition, and with early intervention and access to appropriate resources, individuals can overcome their struggles and pave the way for a healthier, more fulfilling life. By working together and remaining vigilant, we can create a safer and more supportive environment for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
How early can screening tools such as CRAFFT and AUDIT identify potential addiction issues?
Answer: Screening tools like CRAFFT (for adolescents) and AUDIT (for adults) can be used relatively early to identify substance use disorders or problematic patterns. CRAFFT is recommended for ages 12-21, while AUDIT can be used for adults starting from college age onward. Early and regular screening can help catch issues before they escalate.
What should be done if someone refuses to communicate openly or attend educational programs about addiction?
Answer: Lack of open communication or resistance to education can be a challenge. In such cases, focus on creating a non-judgmental environment and addressing any underlying factors like stigma or mistrust. Provide factual information respectfully, and consider involving a trusted third party or counselor to facilitate the process.
How can communities with limited resources leverage external support for early addiction identification?
Answer: Communities with limited resources can explore partnerships with regional or national organizations, nonprofits, and government agencies that offer addiction-related services or funding. Online resources, helplines, and telehealth options can also provide access to professional guidance and support for early identification efforts.
















 Kap’s Cafe in Surrey was struck by gunfire late at night with staff still insideInstagram/
Kap’s Cafe in Surrey was struck by gunfire late at night with staff still insideInstagram/ Kaps Cafe Instagram Story Instagram Screengrab/
Kaps Cafe Instagram Story Instagram Screengrab/ Kaps Cafe Instagram Story Instagram Screengrab/
Kaps Cafe Instagram Story Instagram Screengrab/

