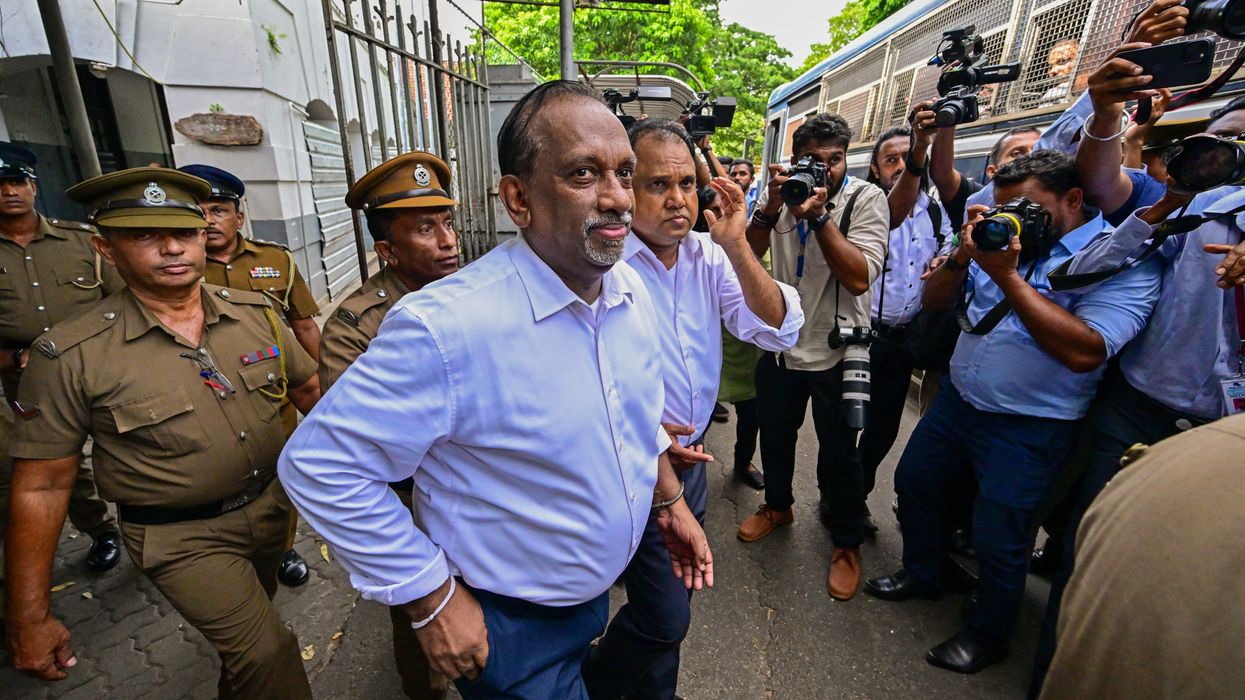A SRI LANKAN court last Thursday (29) sentenced two former ministers from the government of deposed president Gotabaya Rajapaksa to decades in prison in a landmark corruption case.
Ex-sports minister Mahindananda Aluthgamage and former trade minister Anil Fernando were found guilty by the Colombo high court of misappropriating 53 million rupees (£131,121) of state funds.
The pair were also fined £1,481 for using government money to donate board games – including 14,000 carrom boards and 11,000 draughts sets – in an attempt to boost the failed 2015 re-election bid of Gotabaya’s elder brother, Mahinda Rajapaksa.
Aluthgamage was sentenced to 20 years in jail. Fernando was sentenced to 25 years.
Aluthgamage is now the most senior member of a Rajapaksa-led cabinet to be successfully prosecuted for corruption.
The cases against both men were initiated six years ago, when the Rajapaksa brothers were out of power, but the case had been making slow headway until a new government took office last year.
Aluthgamage also faces a separate investigation into allegations that he authorised in 2022 a payment of $6.09 million (£4.5m) to a Chinese supplier for a fertilizer shipment that was never delivered. He caused a stir in 2020 when he accused Sri Lanka’s national cricket team of rigging the 2011 World Cup final in favour of India, triggering a probe that ultimately failed to substantiate his claims.
Aluthgamage, who served as sports minister from 2010 to 2015, said in June 2020 that he had “not wanted to disclose” the alleged match-fixing plot at the time.
“In 2011, we were supposed to win, but we sold the match. I feel I can talk about it now. I am not implicating players, but certain sections were involved,” he said.