THE government’s race report, released last month, could “turn back the clock on the fight against racism,” a healthcare leader has said, as bodies credited in the review distanced themselves from the findings following its publication.
The Commission on Race and Ethnic Disparities (CRED) report, published at the end of March, said the UK “should be regarded as a model for other white-majority countries” and denied institutional racism existed.
Ordered by prime minister Boris Johnson’s government after widespread Black Lives Matter (BLM) protests last summer, it said issues around race and racism were becoming less important in explaining disparities and different outcomes had as much to do with social class and family structure.
There was widespread fury from equality campaigners and MPs who branded the review’s conclusion as a “whitewash” and accused the government of “gaslighting” the experience of minorities.
While putting together the report, the commission apparently heard evidence from numerous organisations who are acknowledged in an appendix. At least 20 have now distanced themselves from the report, including the Consortium of BAME Health Professional Networks which featured support from the British Association of Physicians of Indian Origin (BAPIO).
Dr JS Bamrah, BAPIO’s national chairman, said the report threatened to “turn the clock back on the fight against racism”. “The report says they do not see Britain as a system which is deliberately rigged against ethnic minorities and it just makes you think how out of touch they are,” he told Eastern Eye on Monday (12). “Racism is a serious thing and (the commission) has tried to dumb down the impact of institutional and structural racism within the NHS. (The review) is a huge disappointment.”
In an open letter published on social media last week, BAPIO accused the review of using “inflammatory language” which would “put the lives of BAME communities at further risk”.
“As members of the BAME healthcare professional community, we are dismayed that CRED have not only downplayed the significant impact of racism in British society, but taken an unprecedented step in going further, framing those highlighting systemic and institutional issues as being ‘pessimistic’ and carrying an ‘accusatory tone,’” the letter read.
The open letter also noted the disproportionate deaths of BAME frontline workers during the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic and the Windrush and Grenfell tragedies highlighted the structural barriers existing in society.
“These cannot, and must not, be swept under the carpet by a partisan report that has drawn up spurious conclusions which fly against established facts, derided by global experts, and defies the lived experiences of many,” the letter added. “We urge the government to listen to the many credible experts who have decades of research and policy experience in racial and health inequalities, and not an outlier commission that is out of touch with our communities and reality.”
Other bodies which rejected the report include the British Medical Association (BMA), who argued against the review’s central argument that institutional racism did not exist.
Some experts cited in Downing Street’s race report claimed they were not properly consulted before being named. Historian Stephen Bourne said he was “horrified” to see his name listed, stating he was unaware that a roundtable discussion he attended during Black History Month was linked to the report.
“(After the meeting) I said in the future, you need to be very clear and concise about when you invite people to these things and what they’re going into. It’s disrespectful and it’s unprofessional,” he said. “I didn’t even know they were writing a report until it was published, and I was sort of watching the media and then I downloaded it and discovered to my horror that I was cited as a stakeholder.”
A spokesperson for the commission said: “The commission has examined the evidence and data to come up with solutions that are based on the facts. The commission engaged both directly and indirectly with thousands of researchers, analysts, stakeholders, and members of the public to inform this comprehensive report. We have thanked them as a courtesy.”














 Pedro Pascal addresses fan backlash over playing Reed Richards at 50Getty Images
Pedro Pascal addresses fan backlash over playing Reed Richards at 50Getty Images 
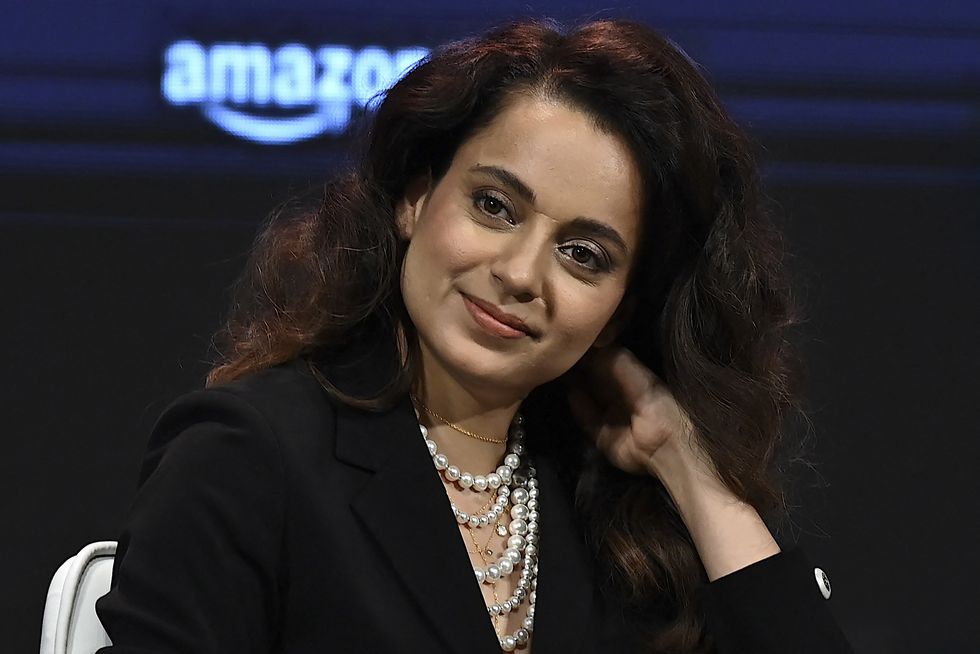 Kangana Ranaut speaks on equality and her role as a ParliamentarianGetty Images
Kangana Ranaut speaks on equality and her role as a ParliamentarianGetty Images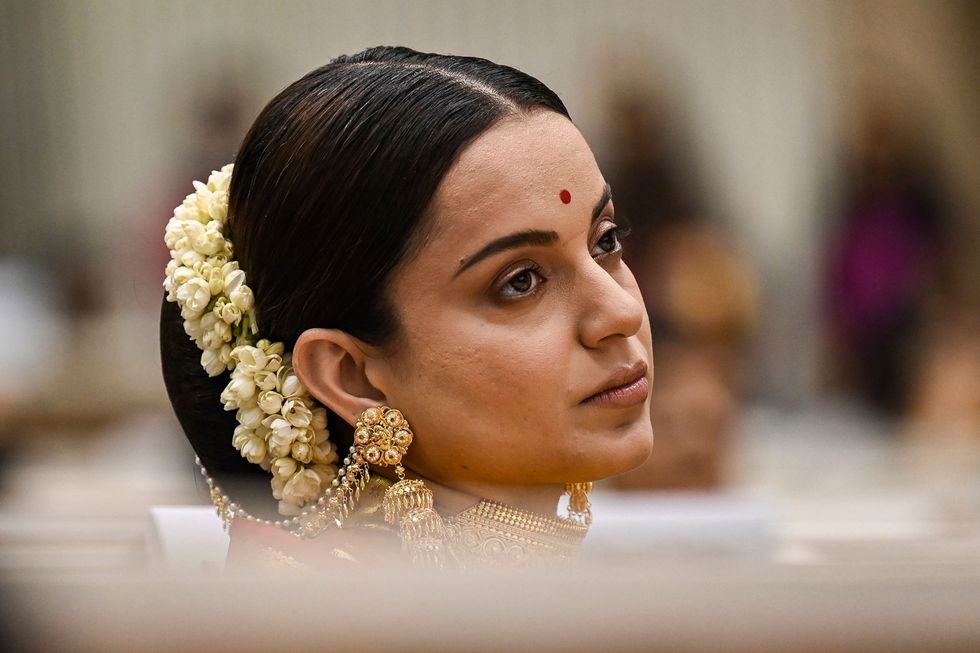  Kangana Ranaut calls equality a flawed idea, claims it’s ruining work ethic in today’s youthGetty Images
Kangana Ranaut calls equality a flawed idea, claims it’s ruining work ethic in today’s youthGetty Images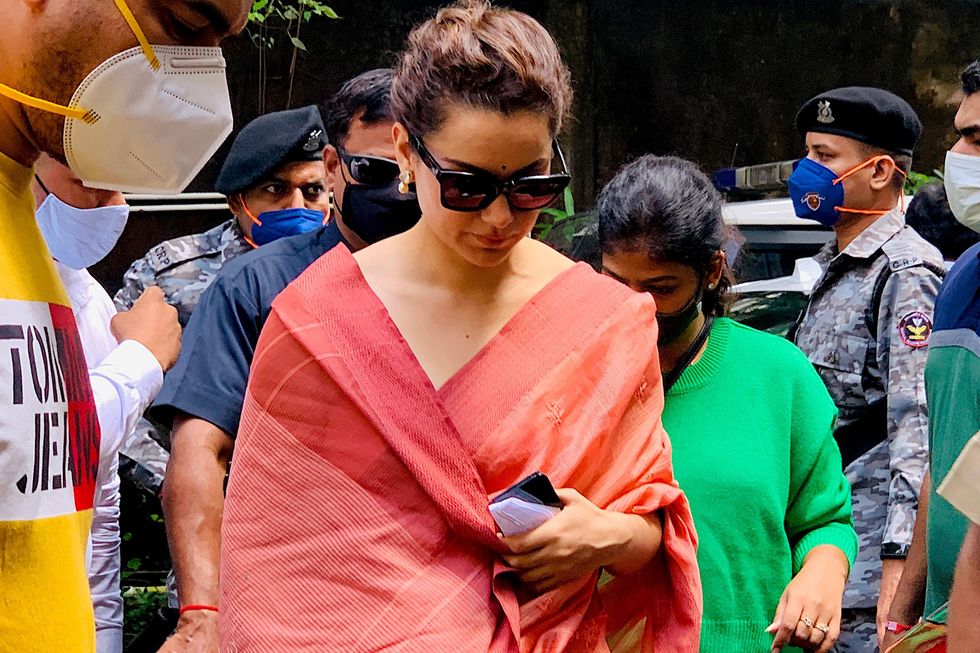 Kangana Ranaut says belief in equality has created a ‘generation of morons’ in viral Times Now interviewGetty Images
Kangana Ranaut says belief in equality has created a ‘generation of morons’ in viral Times Now interviewGetty Images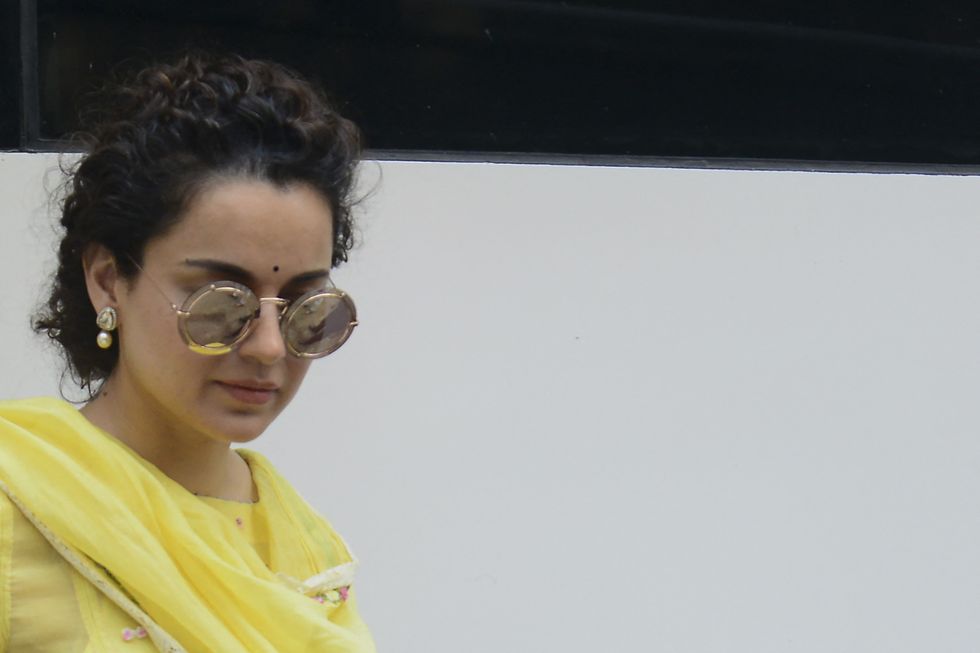 Kangana Ranaut blames equality for entitlement culture, says no two people are equalGetty Images
Kangana Ranaut blames equality for entitlement culture, says no two people are equalGetty Images
 Actress Bella Thorne and Charlie Puth attend the Y100's Jingle Ball 2016Getty Images
Actress Bella Thorne and Charlie Puth attend the Y100's Jingle Ball 2016Getty Images 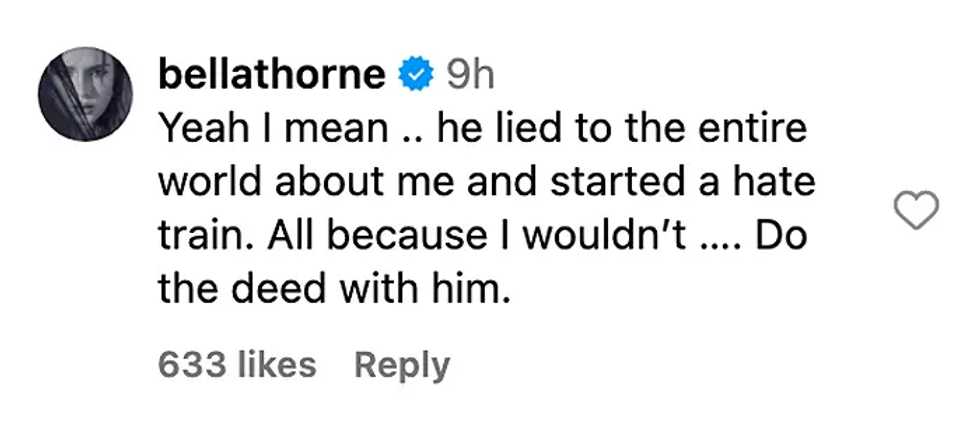 Bella Thorne's commentInstagram Screengrab
Bella Thorne's commentInstagram Screengrab  Charlie Puth performs onstage at an interactive global eConcert liveGetty Images
Charlie Puth performs onstage at an interactive global eConcert liveGetty Images  Bella Thorne and Mark Emms attend a red carpet for the movie "Priscilla"Getty Images
Bella Thorne and Mark Emms attend a red carpet for the movie "Priscilla"Getty Images Charlie Puth and Brooke Sansone attend the 10th Breakthrough Prize CeremonyGetty Images
Charlie Puth and Brooke Sansone attend the 10th Breakthrough Prize CeremonyGetty Images