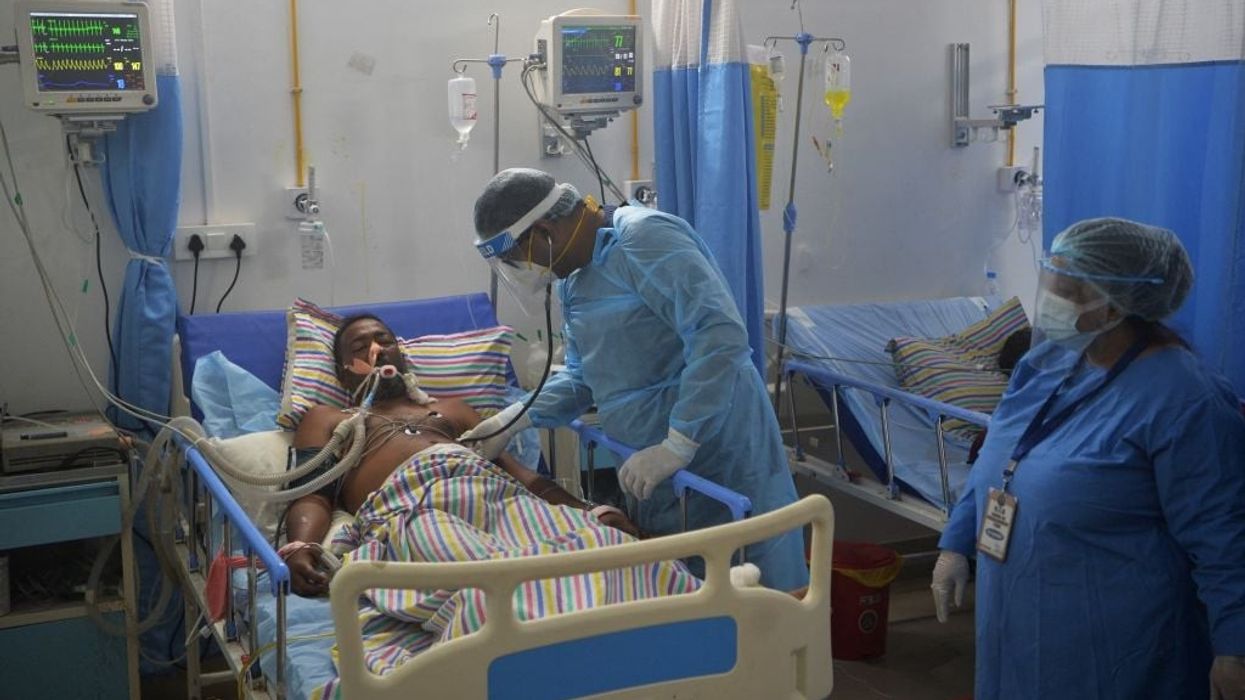
LOW PAY, 24-hour shifts and severe shortages of staff and protective gear have left many doctors on the frontlines of India's brutal pandemic surge near breaking point and fearful for their lives.
Coronavirus infections have killed at least 165,000 people in the vast South Asian nation -- home to some of the world's most densely populated cities -- since the start of April.
Although India's latest Covid-19 surge has eased recently, around 3,000 people are still dying every day and the chronically underfunded health care system remains under severe pressure.
"We are overworked, stressed and very frightened," Radha Jain, a doctor in the capital New Delhi, told AFP.
The Indian Medical Association said more than 1,200 doctors have died of Covid since the start of the pandemic -- including over 500 in the last two months.
Deependra Garg, a doctor working in Delhi's outskirts, knows first-hand how dire the situation has become.
His wife Anubha, 48, a physician herself, fell ill with Covid in April.
They started treatment at home but as her condition worsened, he -- like so many other families -- struggled to get a hospital bed.
He eventually found one almost 200 kilometres (120 miles) from their home. But Anubha -- who was fully vaccinated -- died within two weeks, leaving behind their 12-year-old daughter.
"We are on the frontlines 24/7. We are exposed to a high virus load but we have to continue working against all odds as we have chosen this profession," Garg said.
"We do not have a choice."
Structural weaknesses in healthcare
The pandemic has exposed structural weaknesses in India's healthcare system, particularly in the ill-equipped state-run hospitals.
As the latest outbreak spread, reports emerged from short-staffed hospitals of patients lying on floors and sharing beds in packed wards, as family members protected with only cotton masks took care of their stricken loved ones.
The government spends less than two per cent of GDP on healthcare, one of the lowest rates in the world.
India had just 0.8 doctors per 1,000 people in 2017 -- around the same level as Iraq, according to the World Bank. The two other countries worst-hit by the coronavirus, Brazil and the US, had 2.2 and 2.6 respectively.
A report from before the pandemic by the US-based Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics and Policy estimated that India needed 600,000 more doctors and two million extra nurses to meet its healthcare needs.
Doctor Shekhar Kumar, working with a private hospital in the northern state of Uttar Pradesh, said junior staff and final-year medical students sometimes had to work 24-hour shifts.
"Compared to last year, this time patients are needing longer hospital stays which is increasing the burden on the staff," Kumar said.
He added that they were further stretched when their colleagues fell ill with the virus.
Doctors said they had been traumatised by being forced to choose which patients to save first as they grappled with insufficient supplies of medicine and oxygen.
Ravikant Singh, the founder of a charity group helping to set up Covid field hospitals, said he struggled to sleep some nights.
Even after completing their punishing shifts, doctors said they worried about infecting their families at home.