INDIA and Pakistan both dispatched top parliamentarians to press their cases in the UK and US, where president Donald Trump showed eagerness for diplomacy between them.
After crisscrossing the world, the delegations were last week at the same time in Washington, which said it played a mediatory role in a ceasefire after four days of fighting between India and Pakistan in May.
In similar strategies, the delegations are both led by veteran politicians who have been critical of their countries’ governments and are known for their ease in speaking to Western audiences.
Pakistan embraced an active role for the Trump administration while India, which has close relations with Washington, has been more circumspect and has long refused outside mediation over Kashmir.
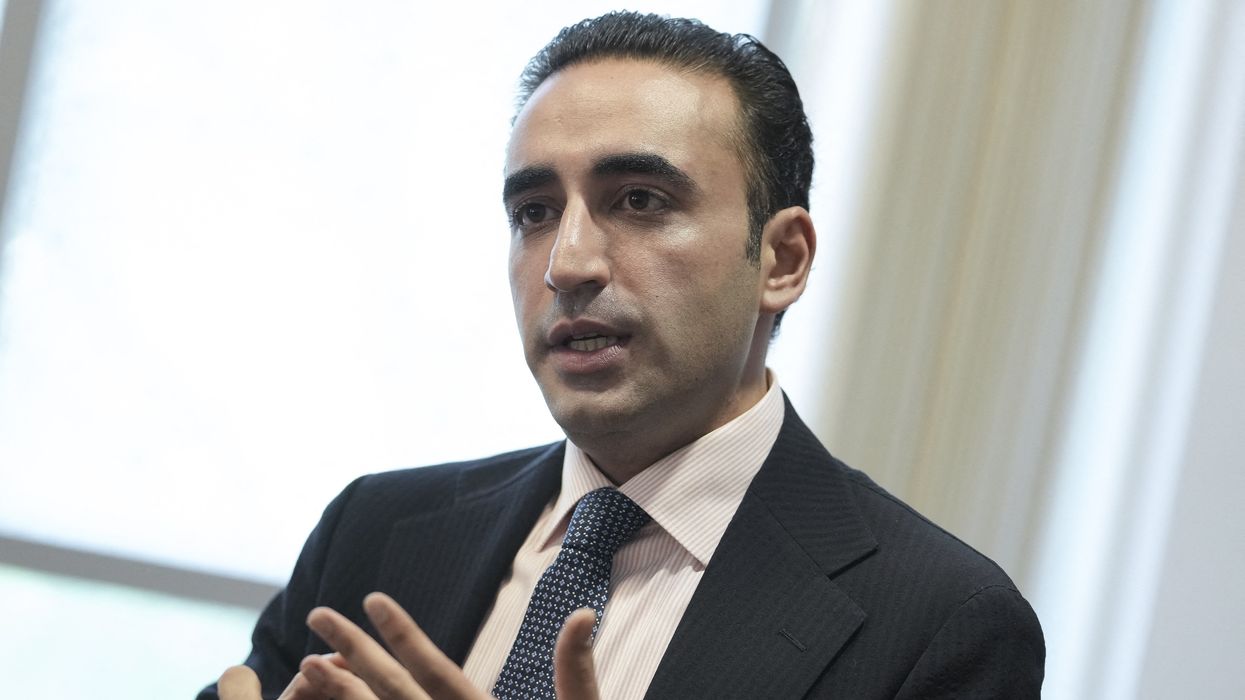
“Just like the United States and president Trump played a role in encouraging us to achieve this ceasefire, I believe they should play their part in encouraging both sides to engage in a comprehensive dialogue,” said Bilawal Bhutto Zardari, of the Pakistan People’s Party, which says it belongs neither to the governing coalition nor opposition.
“I don’t quite understand the Indian government’s hesitance,” he told AFP.
“I’m the first to criticise the United States for so many reasons, but where they do the right thing, where they do the difficult task of actually achieving a ceasefire, they deserve appreciation.”
India’s delegation was led by one of its most prominent opposition politicians, Shashi Tharoor, a former senior UN official and writer.
He said he was putting the national interest first, despite disagreements domestically with prime minister Narendra Modi.
Tharoor said he heard “total support and solidarity for India” during his meetings with US lawmakers and a “complete understanding of India’s right to defend itself against terrorism.”
“There can be no equivalence between a country sending terrorists and a country having its civilians killed – holiday-makers, tourists, men shot down in front of their wives and children after being asked their religion,” Tharoor told a news conference.
He said he was “puzzled” by those who believe denials of responsibility by Pakistan, pointing to how US forces found Osama bin Laden in the country.
Tharoor also noted that former Pakistani president Asif Ali Zardari – Bilawal’s father – had advocated peace with India, but was in power during the siege of Mumbai on November 26, 2008.
“If they can’t control what they’re doing to us, why bother to talk to them?” said Tharoor, who pointed to the outsized role of the military in Pakistan.
Trump has repeatedly credited his administration with averting nuclear war and said the United States had negotiated an agreement to hold talks between the two sides at a neutral site, an assertion that met India’s silence.
Pakistan had cool relations with Trump’s predecessor Joe Biden, whose aides bitterly resented Islamabad’s role in the Afghanistan war, but Pakistan has quickly worked to woo Trump including with the arrest of a suspect in a deadly 2021 attack that killed more than 170 people, including 13 US troops, during the withdrawal from Kabul.
Bilawal – recalling how his mother, former prime minister Benazir Bhutto, was killed in an attack – said Pakistan was ready to discuss terrorism with India, but that Kashmir as a “root cause” also needed to be on the table.
He said India was establishing a dangerous precedent in south Asia where whenever there is a terrorist attack in any country, “you go straight to war.”
“I think that the fate of 1.7 billion people and our two great nations should not be left in the hands of these nameless, faceless, non-state actors and this new normal that India is trying to impose on the region,” he said.
Pakistan’s former foreign secretary, Jalil Abbas Jilani, a member of the delegation, said, “Our message was clear – Pakistan seeks peace.”
Jilani said Islamabad sought the resolution of all issues with India, including the Indus Waters Treaty, through dialogue. Lawmaker Khurram Dastgir highlighted the regional impact of the water dispute and called for the restoration of the 1960 World Bank-mediated treaty, which India said remained in abeyance until Islamabad ended its support for cross-border terrorism.
“We explained to US officials that India’s suspension of the treaty endangers livelihood of 240 million people and undermines the region’s stability,” he said.
Dastgir stressed the water dispute was a matter of survival for Pakistan.
Senator Sherry Rehman, another member of the group, said the mission was focused on advocating for peace and ensuring the water treaty and Kashmir issue remained on the international agenda.