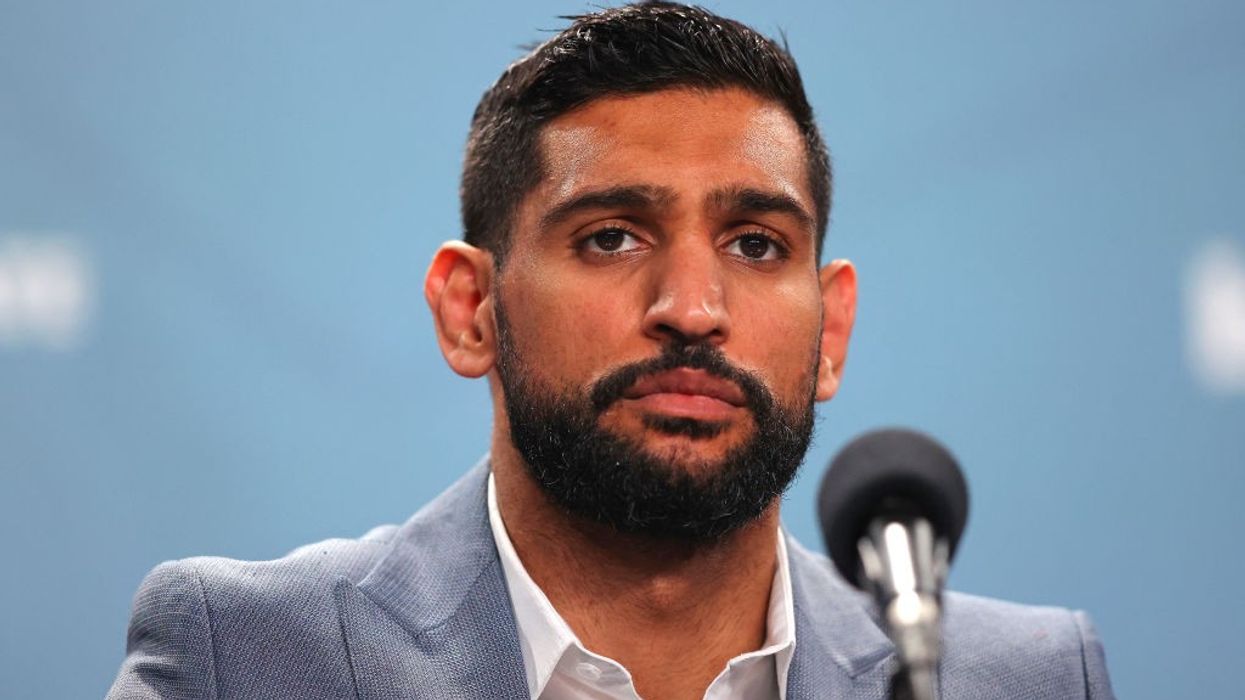
British boxer Amir Khan has been banned from all sport for two years after the prohibited substance ostarine was detected in his sample following his fight against Kell Brook last February, the UK Anti-Doping agency said on Tuesday (4).
Former light-welterweight world champion Khan, 36, announced his retirement in May after his sixth-round stoppage defeat to fellow Briton Brook on Feb. 19 but would be unable to return to the ring until April 2024.
The UKAD website states that ostarine is a drug designed to have similar effects to testosterone. It is present on the World Anti-Doping Agency's prohibited list as an anabolic agent and is prohibited in sport at all times.
Khan, who had expressed concerns over a lack of drug testing before his fight against Brook, accepted that he broke anti-doping rules but said it was not intentional.
An independent tribunal accepted Khan's argument and ruled out "deliberate or reckless conduct" in a written decision dated Feb. 21, 2022, and imposed a two-year ban from all sport due to "strict liability".
"Strict liability means Athletes are ultimately responsible for what they ingest and for the presence of any prohibited substances in a sample," UKAD chief executive Jane Rumble said.
Khan's ban began on April 6, 2022 and will expire on April 5 next year.
(Reuters)